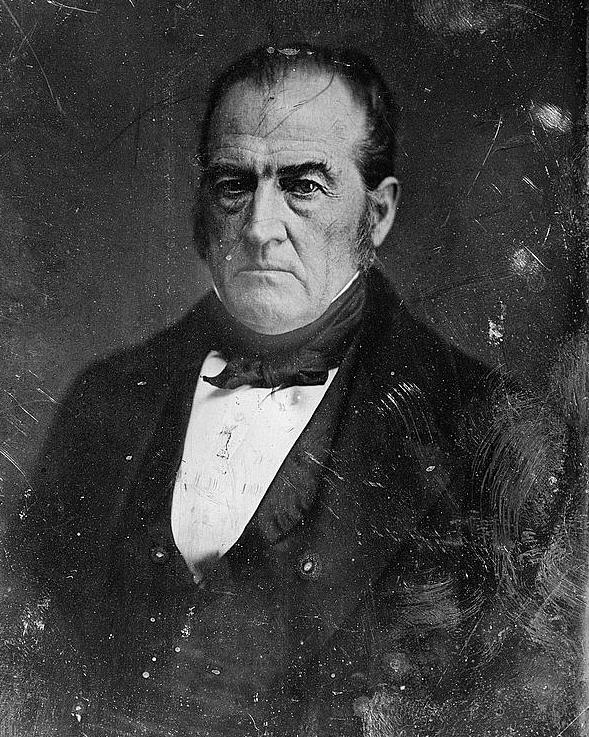
1860 Constitutional Union Convention
The 1860 Constitutional Union National Convention met on May 9, 1860, in Baltimore, Maryland. It was the only national convention ever held by the Constitutional Union Party, which was organized largely by former Whig Party members from the Southern United States who opposed secession. The convention nominated former Senator John Bell of Tennessee for president and former Secretary of State Edward Everett of Massachusetts for vice president.
Convention
Bell won the presidential nomination on the second ballot of the convention, defeating Everett, Governor Sam Houston of Texas, Senator John J. Crittenden of Kentucky, former Governor William Alexander Graham of North Carolina, Associate Justice John McLean of Ohio, and several other candidates. In the 1860 presidential election, Bell and Everett finished third in the electoral vote and fourth in the popular vote.
Background[edit]
After the passage of the Kansas-Nebraska Act in 1854, the Whigs collapsed due to divisions over slavery. Many Northern Whigs shifted to the new Republican Party, while many Southern Whigs joined the American Party, or "Know Nothings."[1]: 304 By 1859, the Know Nothing movement had collapsed, but some former Southern Whigs who refused to join their long-time rivals in the Democratic Party had organized themselves into the "Opposition Party." Several of this party's supporters, among them Knoxville Whig editor William Brownlow, former vice presidential candidate Andrew Jackson Donelson, and California attorney Balie Peyton sought to launch a third-party presidential ticket.[1]: 346
In May 1860, disgruntled ex-Whigs and disenchanted moderates from across the country convened in Baltimore, where they formed the Constitutional Union Party. The party's platform was very broad and made no mention of slavery. While there were several candidates for the party's presidential nomination, the two frontrunners were Bell and Sam Houston.[1]: 354
![John Bell, Tennessee former U.S. Senator[2]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e9/John-bell-brady-handy-cropped_restored.jpg/100px-John-bell-brady-handy-cropped_restored.jpg)
![Sam Houston, Texas Governor[3]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8e/SHouston_2.jpg/81px-SHouston_2.jpg)
![John J. Crittenden, Kentucky U.S. Senator[4]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b2/John_Jordan_Crittenden_-_Brady_1855.jpg/94px-John_Jordan_Crittenden_-_Brady_1855.jpg)
![Edward Everett, Massachusetts former U.S. Senator[5]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/68/SecEdwardEverett.png/86px-SecEdwardEverett.png)
![William A. Graham, North Carolina former U.S. Senator[6]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c6/William_Alexander_Graham_-_Brady-Handy.jpg/92px-William_Alexander_Graham_-_Brady-Handy.jpg)
![William C. Rives, Virginia former U.S. Senator[7]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/55/WilliamCRives.png/93px-WilliamCRives.png)
