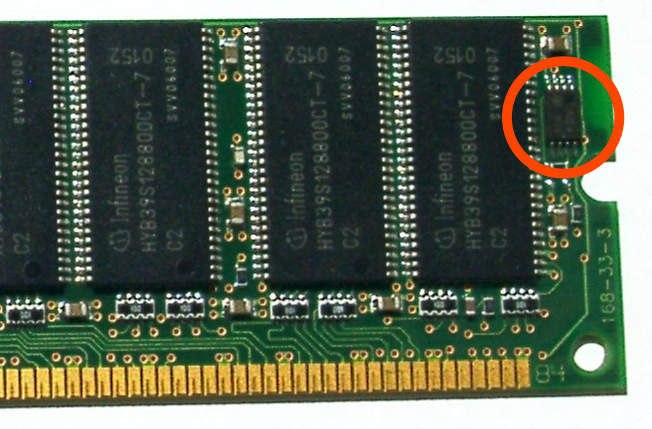
Serial presence detect
In computing, serial presence detect (SPD) is a standardized way to automatically access information about a memory module. Earlier 72-pin SIMMs included five pins that provided five bits of parallel presence detect (PPD) data, but the 168-pin DIMM standard changed to a serial presence detect to encode more information.[1]
When an ordinary modern computer is turned on, it starts by doing a power-on self-test (POST). Since about the mid-1990s, this process includes automatically configuring the hardware currently present. SPD is a memory hardware feature that makes it possible for the computer to know what memory is present, and what memory timings to use to access the memory.
Some computers adapt to hardware changes completely automatically. In most cases, there is a special optional procedure for accessing BIOS parameters, to view and potentially make changes in settings. It may be possible to control how the computer uses the memory SPD data—to choose settings, selectively modify memory timings, or possibly to completely override the SPD data (see overclocking).
On older equipment[edit]
Some older equipment require the use of SIMMs with parallel presence detect (more commonly called simply presence detect or PD). Some of this equipment uses non-standard PD coding, IBM computers and Hewlett-Packard LaserJet and other printers in particular.