Aegis Combat System
The Aegis Combat System is an American integrated naval weapons system, which uses computers and radars to track and guide weapons to destroy enemy targets. It was developed by the Missile and Surface Radar Division of RCA, and it is now produced by Lockheed Martin.
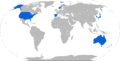
Initially used by the United States Navy, Aegis is now used also by the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force, Spanish Navy, Royal Norwegian Navy, Republic of Korea Navy, and Royal Australian Navy, and is planned for use by the Royal Canadian Navy. As of 2022, a total of 110 Aegis-equipped ships have been deployed, and 71 more are planned (see operators).
Aegis BMD (Ballistic Missile Defense) capabilities are being developed as part of the NATO missile defense system.[1]
The commissioned three Hobart-class destroyers which have Aegis as the core of their combat systems, with the last entering service in 2020. The Australian Government announced that the class of nine Hunter-class frigates to be built in the next decade will also be Aegis equipped, but with a tactical interface developed by Saab Australia.[47] The number of Hunter-class frigates were reduced to 6 following the Australian government's Enhanced Lethality Surface Combatant Fleet program.
Royal Australian Navy
The has awarded Lockheed Martin Canada building 15 Canadian Surface Combatants. The ships will be equipped with the AN/SPY-7(V)1 solid state radar and the International Aegis Fire Control Loop (IAFCL) is integrated with Canada's combat management system, CMS 330, developed by Lockheed Martin Canada for the Royal Canadian Navy's Halifax class ships. The program will make Canada the owner of the world's second largest Aegis fleet.[48]
Royal Canadian Navy
The operates seven Aegis ships comprising the four Kongō-class destroyers that entered service from 1993 and two improved units known as the Atago class from 2007. Two further improved units known as the Maya class were ordered with the first being commissioned in 2020 and the second in 2021.
Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force
The has acquired five Spanish-built Fridtjof Nansen-class frigates equipped with the Aegis system, with the first, HNoMS Fridtjof Nansen entering service in 2006 and the last, HNoMS Thor Heyerdahl, in 2011. One, HNoMS Helge Ingstad was sunk after colliding with an oil tanker. After being raised, it was thought that repairing the ship was too costly and so it was decided to scrap the ship.
Royal Norwegian Navy
currently operates three Sejong the Great-class destroyers, with the lead ship commissioned in 2008. Three further vessels have been ordered.
Republic of Korea Navy
The is currently operating five F100 Álvaro de Bazán-class Aegis frigates, and starting it 2024, it will operate the F110-class frigate[49] as well. The F-110 class will incorporate the International Aegis Fire Control Loop (IAFCL) integrated with SCOMBA, the national combat system developed by Navantia.[48]
Spanish Navy
The currently operates the Aegis equipped Ticonderoga-class cruisers and Arleigh Burke-class destroyers and has ordered more of the latter. It will reportedly integrate the new Aegis Baseline 10 on its upcoming FFG(X) ships [50]
U.S. Navy
Informally, some media refer to the Chinese phased-array radar air-defense destroyers, and Type 052D destroyers, as "Chinese Aegis".[51] Outside foreign observers retain the usage of "Aegis" mainly for the brand-name Aegis Combat System-equipped classes.[52]
Type 052C
Map with Aegis operators in blue
Large screen displays on USS John S. McCain, circa 1997. Destroyers have two displays while cruisers have four.
Wayne E. Meyer
– (United States)
Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense System
– (United Kingdom, France, Italy)
PAAMS
– (United States)
Typhon Combat System
Some destroyers owned by the Chinese Navy equipped with active electronically scanned array and vertical launch systems are also informally called Chinese Aegis (中华神盾), such as , etc.
Type 052D destroyer
U.S. Navy Combat Systems Training, Dahlgren, VA.
Center For Surface Combat Systems (CSCS)
U.S. Navy AEGIS Training, Dahlgren, VA.
AEGIS Training and Readiness Center (ATRC)
in the FAS Military Analysis Network.
AEGIS Weapon System MK-7
in the FAS Military Analysis Network.
DDG-51 ARLEIGH BURKE-class
. The Warfighter Encyclopedia. Warfighter Response Center. October 8, 2003. Archived from the original on November 5, 2004. Retrieved August 10, 2006..
"AN/SPY-1"
. Jane's Information Group. April 25, 2001. Archived from the original on July 1, 2006. Retrieved August 10, 2006.
"AEGIS Weapon System MK-7"
. FIRE CONTROLMAN, VOLUME 02--FIRE CONTROL RADAR FUNDAMENTALS (PDF). US NAVY. Retrieved August 10, 2006.