Basilar membrane
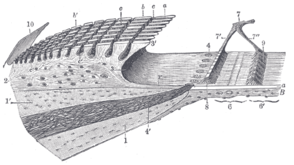
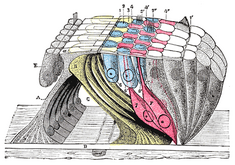
The basilar membrane is a stiff structural element within the cochlea of the inner ear which separates two liquid-filled tubes that run along the coil of the cochlea, the scala media and the scala tympani. The basilar membrane moves up and down in response to incoming sound waves, which are converted to traveling waves on the basilar membrane.
Basilar membrane.
membrana basilaris ductus cochlearis
Structure[edit]
The basilar membrane is a pseudo-resonant structure[1] that, like the strings on an instrument, varies in width and stiffness. But unlike the parallel strings of a guitar, the basilar membrane is not a discrete set of resonant structures, but a single structure with varying width, stiffness, mass, damping, and duct dimensions along its length. The motion of the basilar membrane is generally described as a traveling wave.[2] The properties of the membrane at a given point along its length determine its characteristic frequency (CF), the frequency at which it is most sensitive to sound vibrations. The basilar membrane is widest (0.42–0.65 mm) and least stiff at the apex of the cochlea, and narrowest (0.08–0.16 mm) and stiffest at the base (near the round and oval windows).[3] High-frequency sounds localize near the base of the cochlea, while low-frequency sounds localize near the apex.