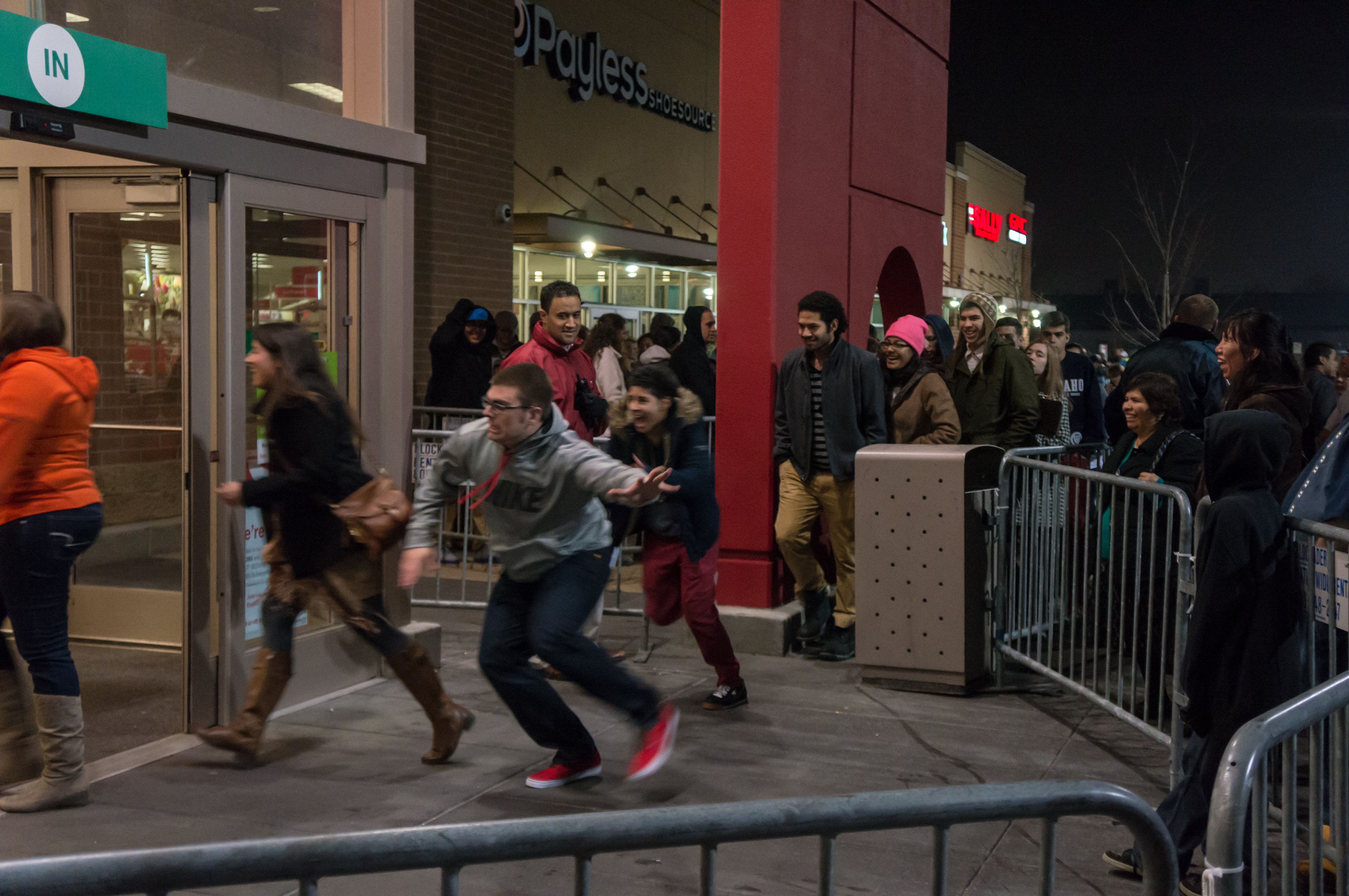
Black Friday (shopping)
Black Friday is the Friday after Thanksgiving in the United States. It traditionally marks the start of the Christmas shopping season in the United States. Many stores offer highly promoted sales at discounted prices and often open early, sometimes as early as midnight[2] or even on Thanksgiving. Some stores' sales continue to Monday ("Cyber Monday") or for a week ("Cyber Week").
Black Friday
Traditionally:[1]
United States
Others:
Australia, Canada, United Kingdom, Ireland, Liechtenstein, Germany, Poland, Italy, Greece, New Zealand, India, Norway, Sweden, France, Spain, Iran, Israel, Brazil, The Netherlands, Mexico (as El Buen Fin) and increasingly in other parts of the world.
Commercial
Popular shopping day
Shopping
Day after U.S. Thanksgiving
November 24
November 29
November 28
November 27
Annual
"Black Friday" has evolved in meaning and impact over the years, initially referring to calamitous days, with a notable early instance being Black Friday (1869) in the US. This financial crisis saw a dramatic plunge in gold prices, affecting investors. The term was later used in American retail, starting ambiguously in the 1950s. Initially associated with workforce absenteeism post-Thanksgiving, it was reinterpreted by Philadelphia police to describe the shopping-induced congestion. Attempts at rebranding to "Big Friday" failed, and the term "Black Friday" solidified by the 1980s, referring to the pivotal point where retailers purportedly shifted from loss ("in the red") to profit ("in the black"). This day marks the unofficial start of the Christmas shopping season, with promotional sales aiming to draw large crowds. Black Friday is the busiest shopping day of the year in the United States[3][4][5] and retailers prioritize it and Cyber Monday as highly profitable holiday shopping days.[6]
The concept has since globalized, with countries around the world adopting "Black Friday" sales to mimic the U.S. phenomenon, adjusting local customs or creating similar events. The advent of online shopping and events like "Cyber Monday" have expanded the traditional one-day shopping frenzy into a broader holiday shopping season, diluting the singular focus of Black Friday, and expanding its economic impact.
Etymology[edit]
For centuries, the adjective "black" has been applied to days upon which calamities occurred. Many events have been described as "Black Friday", although the most significant such event in American history was the Panic of 1869, which occurred when financiers Jay Gould and James Fisk took advantage of their connections with the Grant Administration in an attempt to corner the gold market. When President Grant learned of this manipulation, he ordered the Treasury to release a large supply of gold, which halted the run and caused prices to drop by 18%. Fortunes were made and lost in a single day, and the president's own brother-in-law, Abel Corbin, was ruined.
The earliest known use of "Black Friday" to refer to the day after Thanksgiving occurred in the journal, Factory Management and Maintenance, for November 1951, and again in 1952. Here it referred to the practice of workers calling in sick on the day after Thanksgiving, in order to have a four-day weekend. However, this use does not appear to have caught on. Around the same time, the terms "Black Friday" and "Black Saturday" came to be used by the police in Philadelphia and Rochester to describe the crowds and traffic congestion accompanying the start of the Christmas shopping season. In 1961, the city and merchants of Philadelphia attempted to improve conditions, and a public relations expert recommended rebranding the days "Big Friday" and "Big Saturday", but these terms were quickly forgotten.[7][8][9][10][11][12]
The use of the phrase spread slowly, first appearing in The New York Times on November 29, 1975, in which it still refers specifically to "the busiest shopping and traffic day of the year" in Philadelphia. Although it soon became more widespread, The Philadelphia Inquirer reported in 1985 that retailers in Cincinnati and Los Angeles were still unaware of the term.[13]
As the phrase gained national attention in the early 1980s, merchants objecting to the use of a derisive term to refer to one of the most important shopping days of the year suggested an alternative derivation: that retailers traditionally operated at a financial loss for most of the year (January through November) and made their profit during the holiday season, beginning on the day after Thanksgiving.[7] When this was recorded in the financial records, once-common accounting practices would use red ink to show negative amounts and black ink to show positive amounts. Black Friday, under this theory, is the beginning of the period when retailers would no longer be "in the red", instead of taking in the year's profits.[7][13][14] The earliest known published reference to this explanation occurs in The Philadelphia Inquirer for November 28, 1981.[15]
Since the early 21st century, there have been attempts by U.S.-based retailers to introduce a retail "Black Friday" to other countries around the world. Retailers outside the US have attempted to promote the day to remain competitive with US-based online retailers.[16]
In more recent decades, global retailers have adopted the term and date to market their own holiday sales.[17]