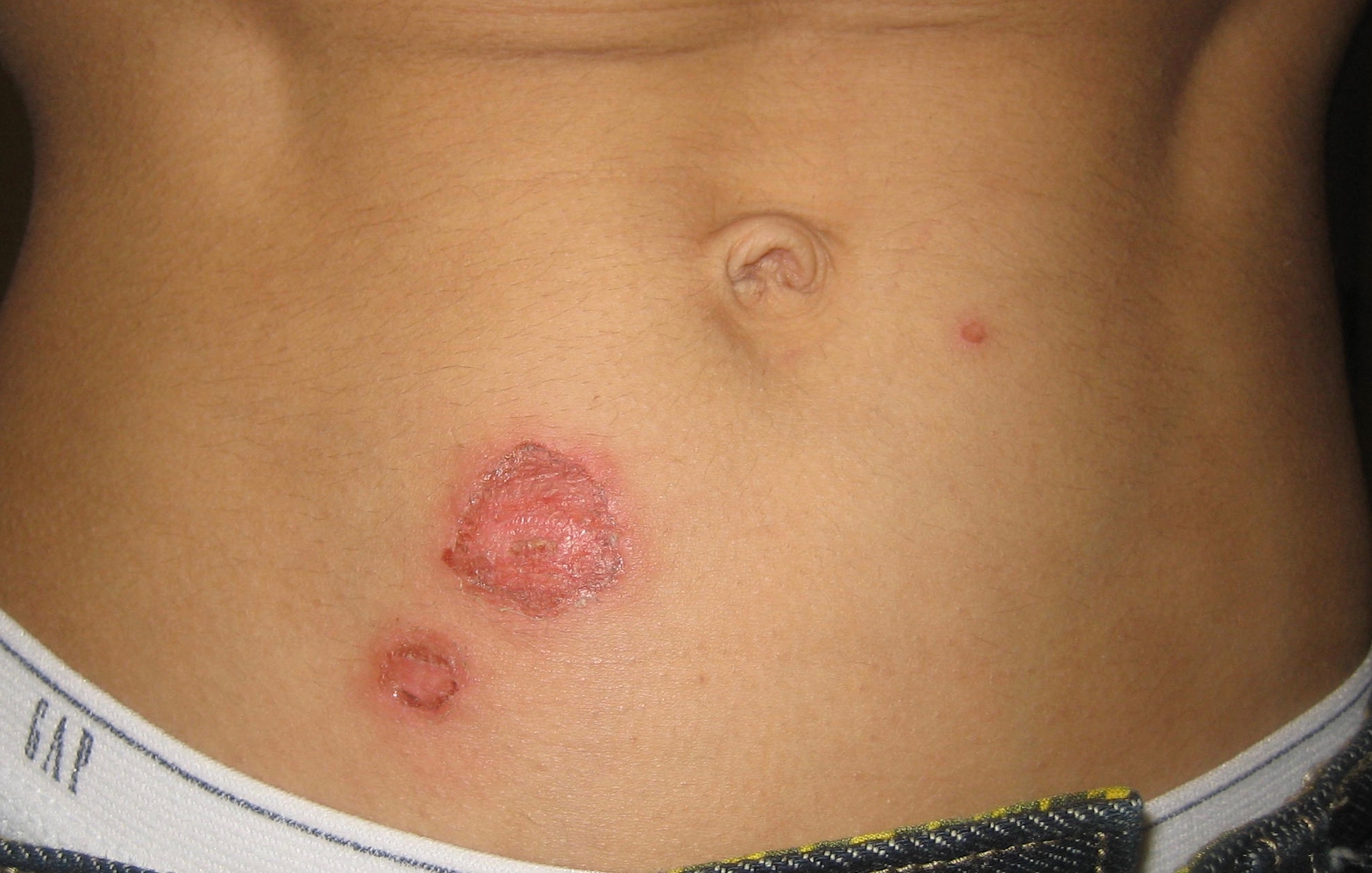
Bullous impetigo
Bullous impetigo is a bacterial skin infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus that results in the formation of large blisters called bullae, usually in areas with skin folds like the armpit, groin, between the fingers or toes, beneath the breast, and between the buttocks. It accounts for 30% of cases of impetigo, the other 70% being non-bullous impetigo.[1]
Bullous impetigo
Infectious disease/dermatology
The bullae are caused by exfoliative toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus that cause the connections between cells in the uppermost layer of the skin to fall apart.[1] Bullous impetigo in newborns, children, or adults who are immunocompromised and/or are experiencing kidney failure, can develop into a more severe and generalized form called staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS). The mortality rate is less than 3% for infected children, but up to 60% in adults.[2]
Prevention[edit]
Since the common pathogens involved with impetigo are bacteria naturally found on the skin, most prevention (especially in children), is targeted towards appropriate hygiene, wound cleaning, and minimizing scratching (i.e. by keeping nails trimmed and short). Avoiding close contact and sharing of items such as towels with potentially infected individuals is also recommended.
Management[edit]
Antibiotic creams are the preferred treatment for mild cases of impetigo, despite their limited systemic absorption. Such prescribed ointments include neosporin, fusidic acid, chloramphenicol and mupirocin. More severe cases of impetigo however (especially bullous impetigo) will likely require oral agents with better systemic bioavailability, such as cephalexin. Cases that do not resolve with initial antibiotic therapy or require hospitalization may also be indicative an MRSA infection, which would require consultation with a local microbiologist.
[7]
Antibiotic treatment typically last 7–10 days, and although highly effective some cases of methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA) may require longer therapy depending on the severity of infection and how much it has spread.