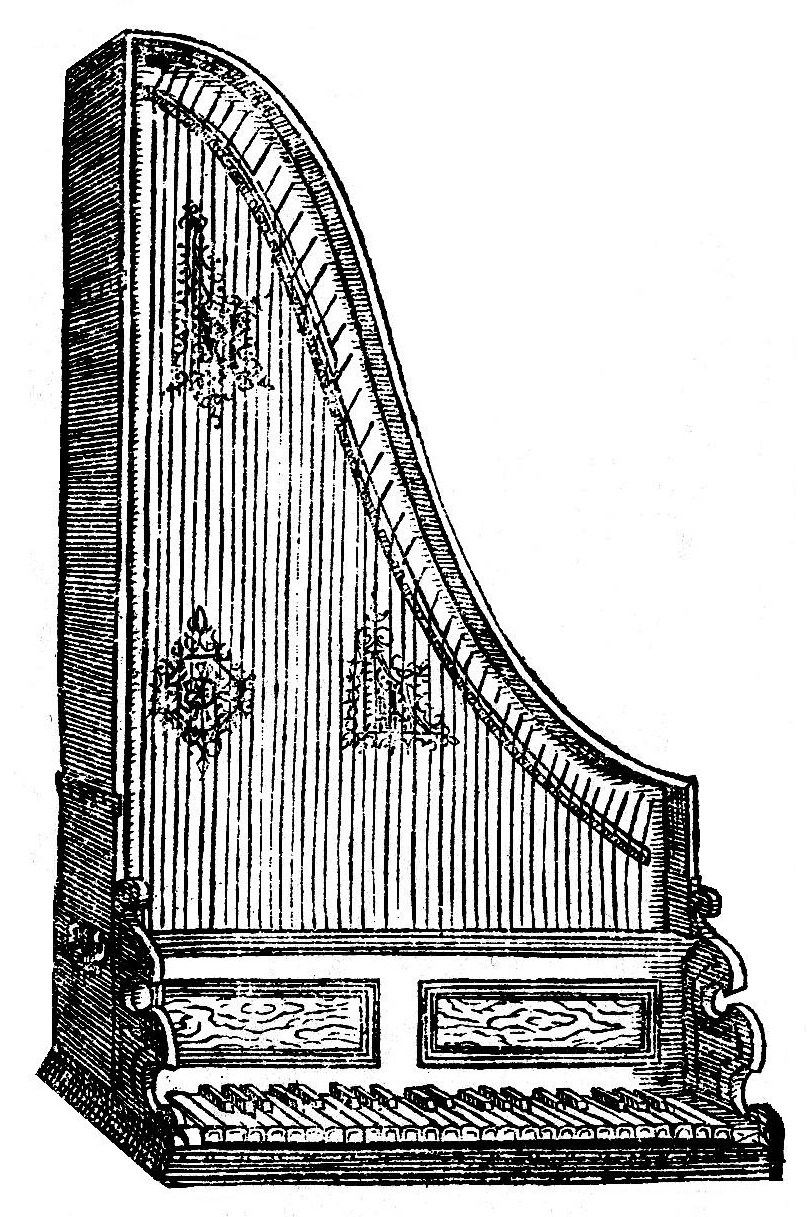
Clavicytherium
A clavicytherium is a harpsichord in which the soundboard and strings are mounted vertically[1] facing the player. The primary purpose of making a harpsichord vertical is the same as in the later upright piano, namely to save floor space. In a clavicytherium, the jacks move horizontally without the assistance of gravity, so that clavicytherium actions are more complex than those of other harpsichords.
Design[edit]
In any harpsichord, the strings are plucked by small plectra, held by jacks, which are thin strips of wood. In a standard harpsichord, the strings are placed horizontally and the jacks are vertical. Thus to make the jack return to position (after it has been lifted by a key to pluck) is a simple matter of gravity; with proper adjustment the jack will simply fall back into its rest position (for details and diagrams see harpsichord).
A clavicytherium sacrifices this simplicity and must find some other means to make the jacks return. In some instruments, this is accomplished with a spring. Another possibility is to couple the jack mechanically to other portions of the action (e.g. keys, levers) that do return by gravity, pulling the jacks back with them.[2] Inevitably, neither strategy is as simple as the direct vertical drop of the jacks in a standard harpsichord. Indeed, finding a good design for a clavicytherium action is not easy, and builders repeatedly sought better solutions. Van der Meer writes, "no standard was ever devised, and there are nearly as many variations of it as there are instruments in existence."[3] Many designs were rather unsuccessful: Ripin reports that clavicytheria often have "a fairly heavy touch and unresponsive action".[4] Describing the unusually fine clavicytheria of Delin (see below), Kottick observes "the action feels quite good to the fingers, which is not a statement one can always make about a clavicytherium."[5]
A special property of clavicytheria is that the player is seated directly in front of the soundboard, at close range. Kottick notes, "[in] all clavicytheria, close proximity to the soundboard provides the player with an overwhelming sense of sonic immersion."[6] Indeed, the modern builder William Horn suggests that it is this esthetic end, not space-saving, that is the primary justification for making clavicytheria.[7]
In shape, clavicytheria were normally like ordinary harpsichords, with the left side longer than the right to accommodate the long bass strings. Occasionally, symmetrical clavicytheria were made, with two bent sides and the peak in the middle; this is sometimes called a "pyramid" shape. The pyramidal design was a challenge to builders, as Ripin notes: "Difficulties arise, since the longer bass strings are in the middle and the treble strings are at the sides, and system of intermediate levels (rollerboard) is required to permit each key to play the correct string unless diagonal stringing is used."[8]
Except in the early period of their construction, clavicytheria were tall. William Horn warns potential buyers that they will need 280 cm. of room below their ceilings (nine feet two inches) to accommodate his Delin replica.[9] The Instrument Workshop, offering plans for a Delin-based instrument, actually reduces its height to 262 cm. (eight feet seven inches) in order to "adapt Delin’s design to modern interiors".[10]
Nomenclature[edit]
Keyboard instrument scholar A. J. Hipkins attributed the name "clavicytherium" to Virdung. It is a Latino-Greek compound, from Latin clavis 'key' and Greek cythara; the latter denoted a variety of stringed instruments.[24]
In other languages the instrument is called clavecin vertical (French), Klaviziterium (German), cembalo verticale (Italian).