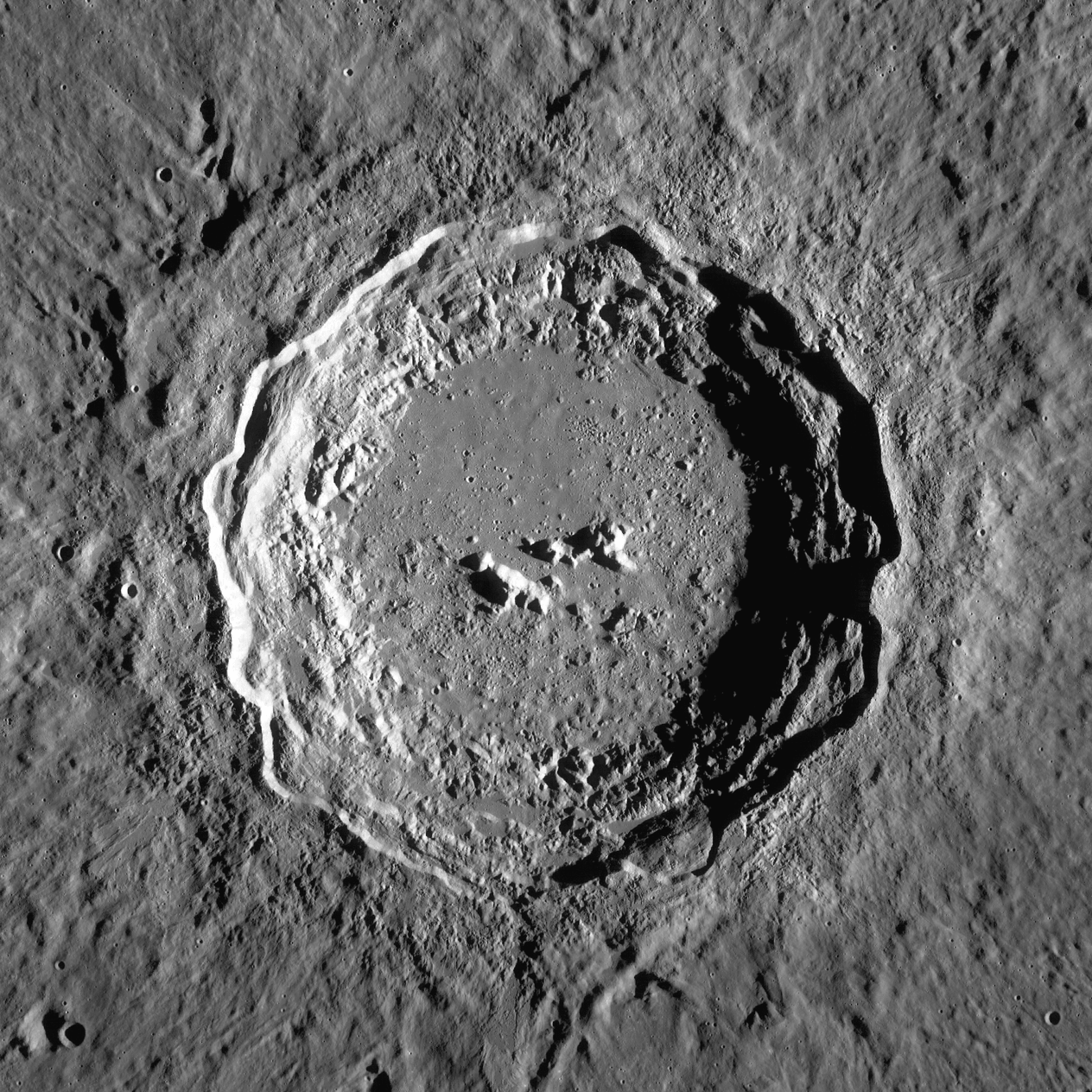
Copernicus (lunar crater)
Copernicus is a lunar impact crater located in eastern Oceanus Procellarum. It was named after the astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus.[1] It typifies craters that formed during the Copernican period in that it has a prominent ray system. It may have been created by debris from the breakup of the parent body of asteroid 495 Eulalia 800 million years ago.[2]
This article is about the crater on the Moon. For the crater on Mars, see Copernicus (Martian crater).
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Copernicus.
Copernicus H, a typical "dark-halo" crater, was a target of observation by Lunar Orbiter 5 in 1967. Dark-halo craters were once believed to be volcanic in origin rather than the result of impacts. The Orbiter image showed that the crater had blocks of ejecta like other craters of similar size, indicating an impact origin. The halo results from excavation of darker material (mare basalt) at depth.[11]


