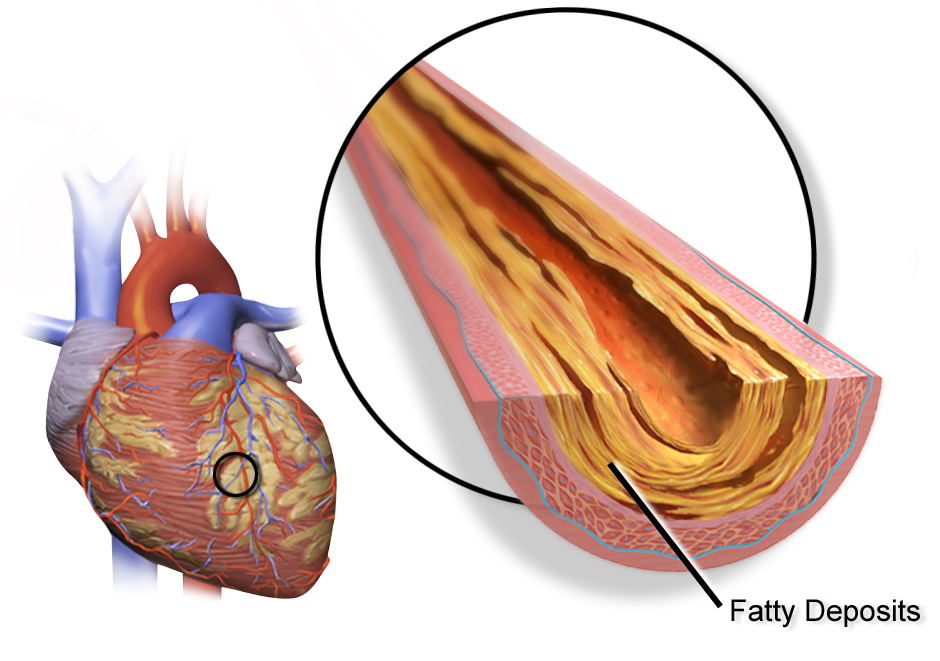
Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD),[13] myocardial ischemia,[14] or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart.[5][6][15] It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases.[16] Types include stable angina, unstable angina, and myocardial infarction.[17]
Coronary artery disease
Healthy diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking[9]
110 million (2015)[11]
8.9 million (2015)[12]
A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw.[4] Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest.[4] Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present.[4] In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack.[5] Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat.[5]
Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, depression, and excessive alcohol consumption.[6][7][18] A number of tests may help with diagnoses including: electrocardiogram, cardiac stress testing, coronary computed tomographic angiography, biomarkers (high-sensitivity cardiac troponins) and coronary angiogram, among others.[8][19]
Ways to reduce CAD risk include eating a healthy diet, regularly exercising, maintaining a healthy weight, and not smoking.[20][9] Medications for diabetes, high cholesterol, or high blood pressure are sometimes used.[9] There is limited evidence for screening people who are at low risk and do not have symptoms.[21] Treatment involves the same measures as prevention.[10][22] Additional medications such as antiplatelets (including aspirin), beta blockers, or nitroglycerin may be recommended.[10] Procedures such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) may be used in severe disease.[10][23] In those with stable CAD it is unclear if PCI or CABG in addition to the other treatments improves life expectancy or decreases heart attack risk.[24]
In 2015, CAD affected 110 million people and resulted in 8.9 million deaths.[11][12] It makes up 15.6% of all deaths, making it the most common cause of death globally.[12] The risk of death from CAD for a given age decreased between 1980 and 2010, especially in developed countries.[25] The number of cases of CAD for a given age also decreased between 1990 and 2010.[26] In the United States in 2010, about 20% of those over 65 had CAD, while it was present in 7% of those 45 to 64, and 1.3% of those 18 to 45;[27] rates were higher among males than females of a given age.[27]
Society and culture[edit]
Support groups[edit]
The Infarct Combat Project (ICP) is an international nonprofit organization founded in 1998 which tries to decrease ischemic heart diseases through education and research.[137]
Industry influence on research[edit]
In 2016 research into the archives of the Sugar Association, the trade association for the sugar industry in the US, had sponsored an influential literature review published in 1965 in the New England Journal of Medicine that downplayed early findings about the role of a diet heavy in sugar in the development of CAD and emphasized the role of fat; that review influenced decades of research funding and guidance on healthy eating.[138][139][140][141]