Corpus cavernosum penis
corpus cavernosum penis
It is homologous to the corpus cavernosum clitoridis in the female.
Structure[edit]
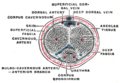
The corpora cavernosa are two expandable erectile tissues along the length of the penis, which fill with blood during penile erection. The two corpora cavernosa lie along the penile shaft, from the pubic bones to the head of the penis, where they join. These formations are made of a sponge-like tissue containing trabeculae, irregular blood-filled spaces lined by endothelium and separated by septum of the penis.[6][7]
The male anatomy has no vestibular bulbs, but instead a corpus spongiosum, a smaller region of erectile tissue along the bottom of the penis, which contains the urethra and forms the glans penis.