Eastern Zhou
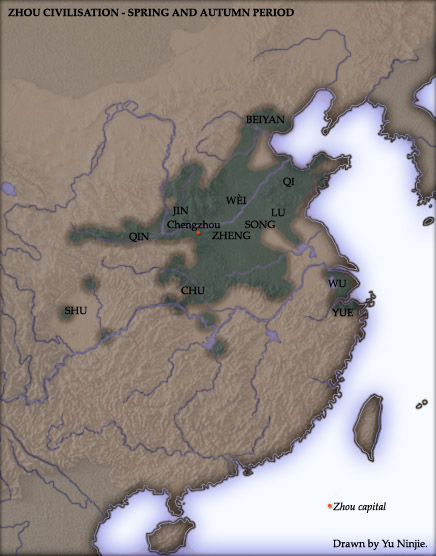
The Eastern Zhou[a] is a period in Chinese history comprising the latter half of the Zhou dynasty from c. 771 BCE to 256 BCE, following the Zhou capital's relocation eastward to Chengzhou, near present-day Luoyang. The Eastern Zhou was characterised by the weakened authority of the Zhou royal house, it is subdivided into two parts: the Spring and Autumn period (c. 771 – c. 481 BCE), during which the ancient aristocracy still held power in a large number of separate polities, and the Warring States period (c. 481 – 221 BCE), which saw the consolidation of territory and escalation of interstate warfare and administrative sophistication.
For a state during the Warring States period, see Eastern Zhou (state).Politics[edit]
The dominant material for making tools had become iron by the end of the Eastern Zhou; as such, it is considered to be the beginning of the Iron Age in China. There was a considerable development in agriculture with a consecutive increase in population. There were constantly fights between vassals to scramble for lands or other resources. People started using copper coins. Education was made universal for civilians. The boundaries between the nobility and the civilians subsided. A revolutionary transformation of the society was taking place, to which the patriarchal clan system made by the Zhou Dynasty could no longer adapt.[6]