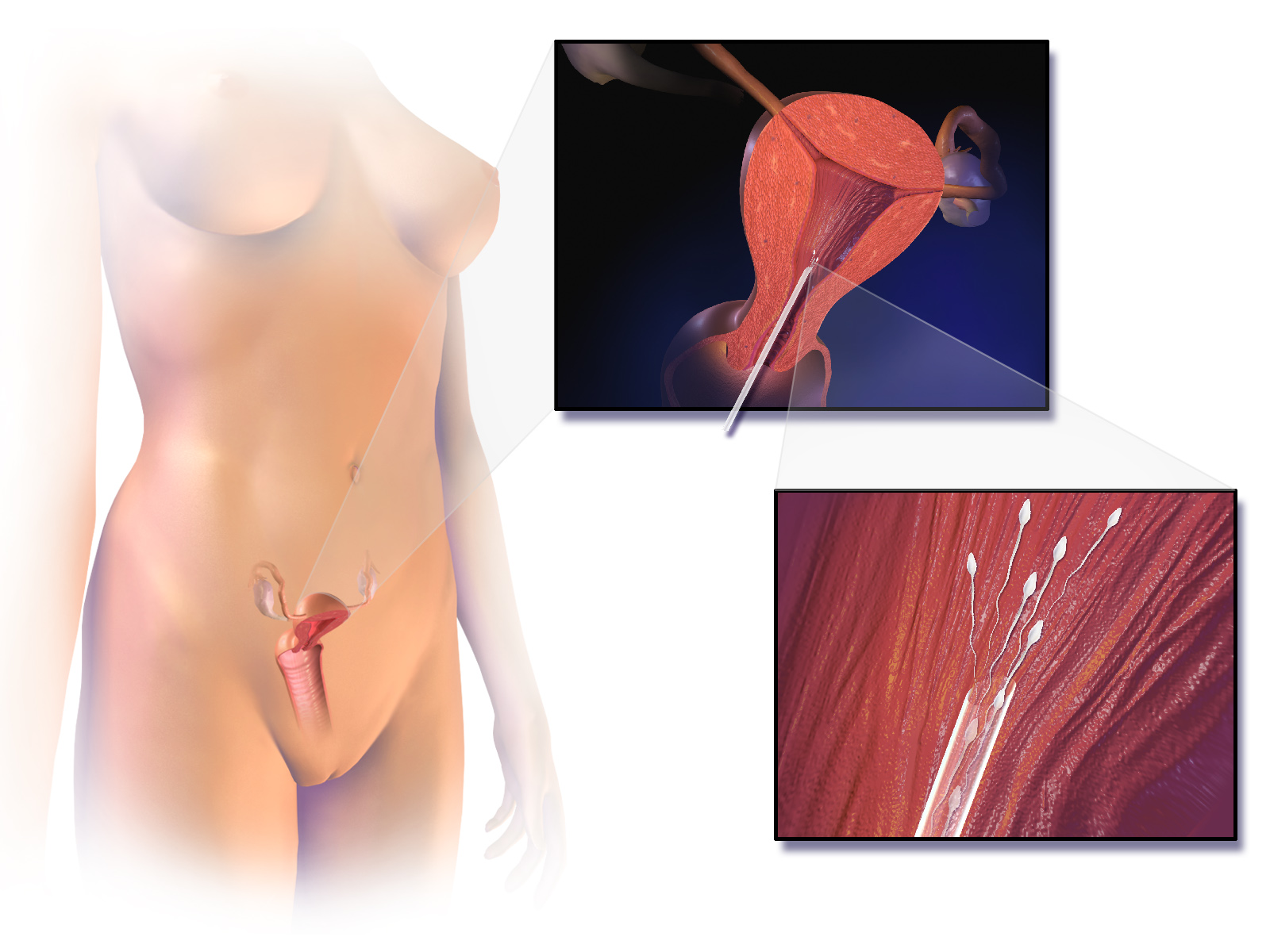
Artificial insemination
Artificial insemination is the deliberate introduction of sperm into a female's cervix or uterine cavity for the purpose of achieving a pregnancy through in vivo fertilization by means other than sexual intercourse. It is a fertility treatment for humans, and is a common practice in animal breeding, including dairy cattle (see frozen bovine semen) and pigs.
"IUI" redirects here. For other uses, see IUI (disambiguation).Artificial insemination may employ assisted reproductive technology, sperm donation and animal husbandry techniques. Artificial insemination techniques available include intracervical insemination (ICI) and intrauterine insemination (IUI). Where gametes from a third party are used, the procedure may be known as 'assisted insemination'.