Law of effect
The law of effect, or Thorndike's law, is a psychology principle advanced by Edward Thorndike in 1898 on the matter of behavioral conditioning (not then formulated as such) which states that "responses that produce a satisfying effect in a particular situation become more likely to occur again in that situation, and responses that produce a discomforting effect become less likely to occur again in that situation."[1]
This notion is very similar to that of the evolutionary theory, if a certain character trait provides an advantage for reproduction then that trait will persist.[2] The terms "satisfying" and "dissatisfying" appearing in the definition of the law of effect were eventually replaced by the terms "reinforcing" and "punishing," when operant conditioning became known. "Satisfying" and "dissatisfying" conditions are determined behaviorally, and they cannot be accurately predicted, because each animal has a different idea of these two terms than another animal. The new terms, "reinforcing" and "punishing" are used differently in psychology than they are colloquially. Something that reinforces a behavior makes it more likely that that behavior will occur again, and something that punishes a behavior makes it less likely that behavior will occur again.[3]
Thorndike's law of effect refutes the ideas George Romanes' book Animal Intelligence, stating that anecdotal evidence is weak and is typically not useful. The book stated that animals, like humans, think things through when dealing with a new environment or situation. Instead, Thorndike hypothesized that animals, to understand their physical environment, must physically interact with it using trial and error, until a successful result is obtained. This is illustrated in his cat experiment, in which a cat is placed in a shuttlebox and eventually learns, by interacting with the environment of the box, how to escape.[4]
History[edit]
This principle, discussed early on by Lloyd Morgan, is usually associated with the connectionism of Edward Thorndike, who said that if an association is followed by a "satisfying state of affairs" it will be strengthened and if it is followed by an "annoying state of affairs" it will be weakened.[5][6]
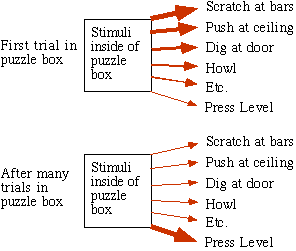
The modern version of the law of effect is conveyed by the notion of reinforcement as it is found in operant conditioning. The essential idea is that behavior can be modified by its consequences, as Thorndike found in his famous experiments with hungry cats in puzzle boxes. The cat was placed in a box that could be opened if the cat pressed a lever or pulled a loop. Thorndike noted the amount of time it took the cat to free itself on successive trials in the box. He discovered that during the first few trials the cat would respond in many ineffective ways, such as scratching at the door or the ceiling, finally freeing itself with the press or pull by trial-and-error. With each successive trial, it took the cat, on average, less and less time to escape. Thus, in modern terminology, the correct response was reinforced by its consequence, release from the box.[7]
Influence[edit]
The law of work for psychologist B. F. Skinner almost half a century later on the principles of operant conditioning, "a learning process by which the effect, or consequence, of a response influences the future rate of production of that response."[1] Skinner would later use an updated version of Thorndike's puzzle box, called the operant chamber, or Skinner box, which has contributed immensely to our perception and understanding of the law of effect in modern society and how it relates to operant conditioning. It has allowed a researcher to study the behavior of small organisms in a controlled environment.
An example of Thorndike’s Law of Effect in a child’s behavior could be the child receiving praise and a star sticker for tidying up their toys. The positive reinforcement (praise and sticker) encourages the repetition of the behavior (cleaning up), illustrating the Law of Effect in action.