Pelvic cavity
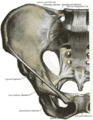
The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet (the superior opening of the pelvis). Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.
Pelvic cavity
The pelvic cavity primarily contains the reproductive organs, urinary bladder, distal ureters, proximal urethra, terminal sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal. In females, the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries and upper vagina occupy the area between the other viscera.[1][2]
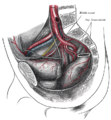
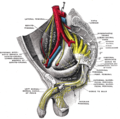
The rectum is located at the back of the pelvis, in the curve of the sacrum and coccyx; the bladder is in front, behind the pubic symphysis. The pelvic cavity also contains major arteries, veins, muscles, and nerves. These structures coexist in a crowded space, and disorders of one pelvic component may impact upon another; for example, constipation may overload the rectum and compress the urinary bladder, or childbirth might damage the pudendal nerves and later lead to anal weakness.