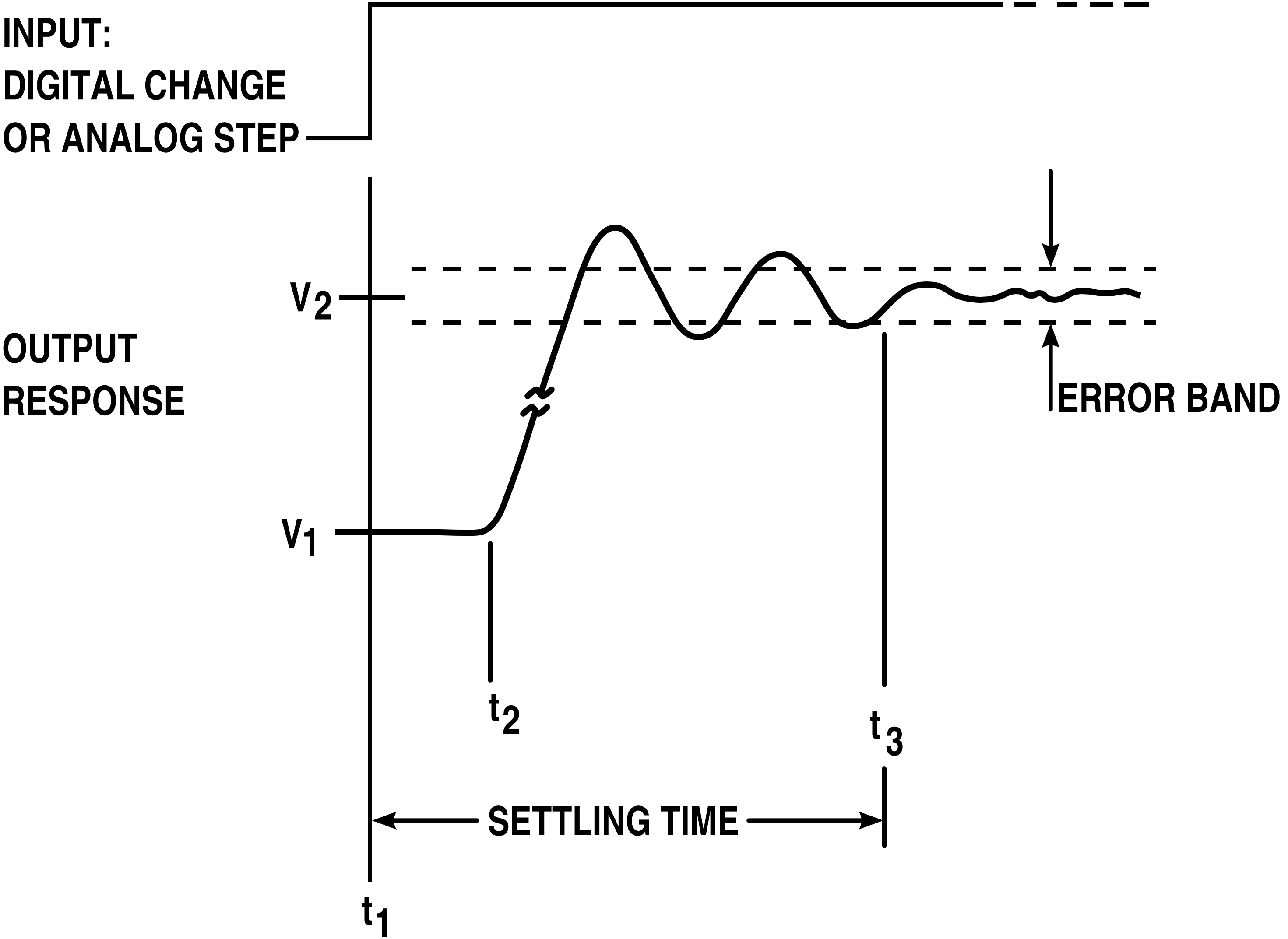
Ringing (signal)
In electronics, signal processing, and video, ringing is oscillation of a signal, particularly in the step response (the response to a sudden change in input). Often ringing is undesirable, but not always, as in the case of resonant inductive coupling. It is also known as hunting.[1]
This article is about ringing in electronics and signals generally. For ringing artifacts in signal processing, particularly image processing, see ringing artifacts. For Ringing in telephony, see Ringing (telephony).It is also known as ripple, particularly in electricity or in frequency domain response.
Analog video[edit]
In a cathode-ray tube (CRT) video circuit, electrical ringing causes closely spaced repeated ghosts of a vertical or diagonal edge where dark changes to light or vice versa, going from left to right, whereby the electron beam's intensity overshoots and undershoots the desired intensity there a few times instead of settling quickly. This bouncing could occur anywhere in the electronics or cabling and is often caused by or accentuated by a too high setting of the sharpness control.
Analog audio[edit]
Ringing can affect audio equipment in a number of ways. Audio amplifiers can produce ringing depending on their design, although the transients that can produce such ringing rarely occur in audio signals.
Transducers (i.e., microphones and loudspeakers) can also ring. Mechanical ringing is more of a problem with loudspeakers as the moving masses are larger and less easily damped, but unless extreme they are difficult to audibly identify.