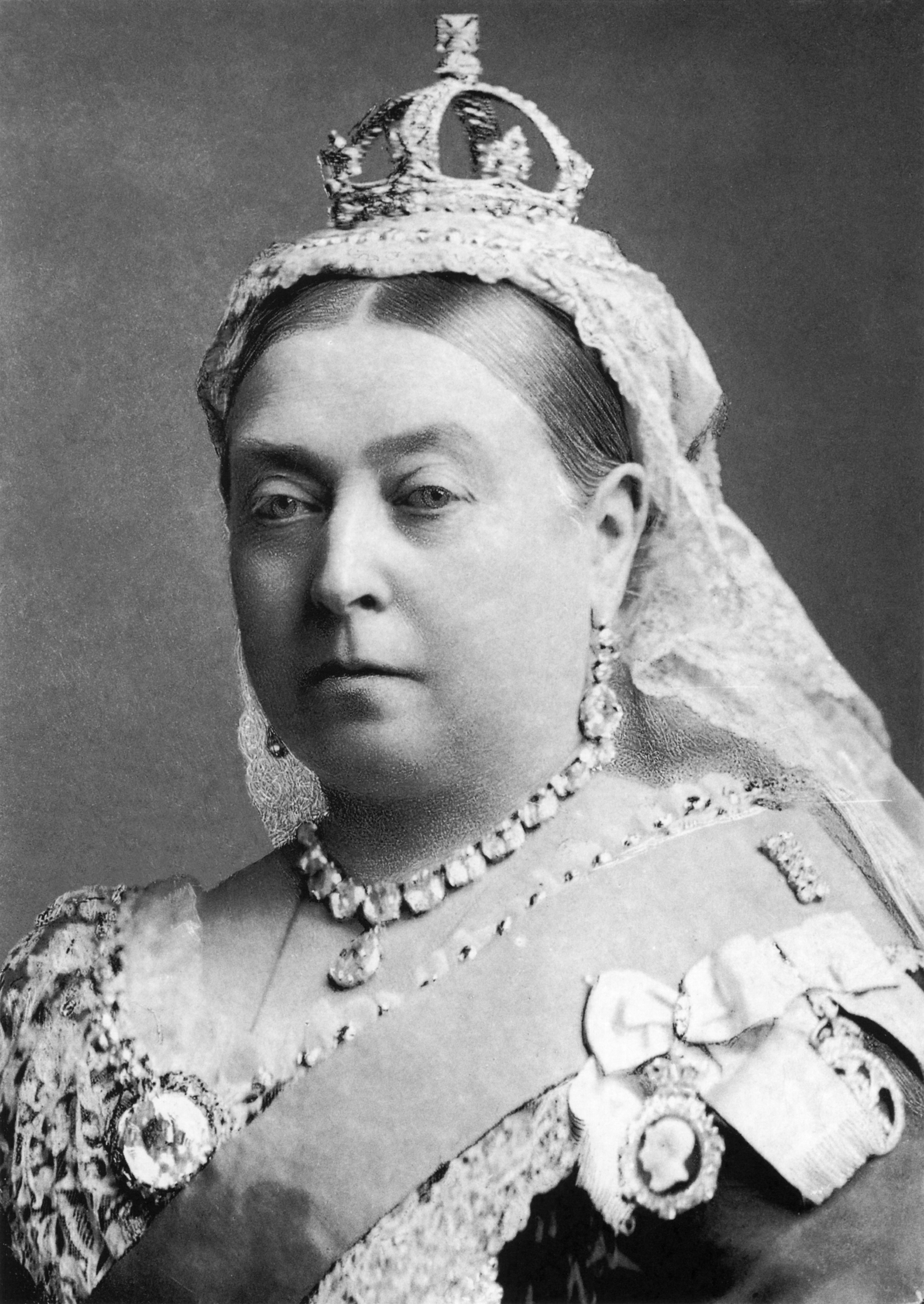
Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days—which was longer than those of any of her predecessors—constituted the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India.
"Victoria of the United Kingdom" and "Victoria I" redirect here. For other people, see Victoria of the United Kingdom (disambiguation) and Queen Victoria (disambiguation). For other uses, see Victoria (disambiguation).Victoria
20 June 1837 – 22 January 1901
28 June 1838
1 May 1876 – 22 January 1901
1 January 1877
Position established
Edward VII
Princess Alexandrina Victoria of Kent
24 May 1819
Kensington Palace, London, England
22 January 1901 (aged 81)
Osborne House, Isle of Wight, England
4 February 1901
- Victoria, German Empress
- Edward VII
- Alice, Grand Duchess of Hesse and by Rhine
- Alfred, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
- Helena, Princess Christian of Schleswig-Holstein
- Princess Louise, Duchess of Argyll
- Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn
- Prince Leopold, Duke of Albany
- Beatrice, Princess Henry of Battenberg
Victoria was the daughter of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (the fourth son of King George III), and Princess Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. After the deaths of her father and grandfather in 1820, she was raised under close supervision by her mother and her comptroller, John Conroy. She inherited the throne aged 18 after her father's three elder brothers died without surviving legitimate issue. Victoria, a constitutional monarch, attempted privately to influence government policy and ministerial appointments; publicly, she became a national icon who was identified with strict standards of personal morality.
Victoria married her first cousin, Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, in 1840. Their nine children married into royal and noble families across the continent, earning Victoria the sobriquet "grandmother of Europe". After Albert's death in 1861, Victoria plunged into deep mourning and avoided public appearances. As a result of her seclusion, British republicanism temporarily gained strength, but in the latter half of her reign, her popularity recovered. Her Golden and Diamond jubilees were times of public celebration. Victoria died at Osborne House on the Isle of Wight, at the age of 81. The last British monarch of the House of Hanover, she was succeeded by her son Edward VII of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha.
Titles, styles, honours, and arms
Titles and styles
At the end of her reign, the Queen's full style was: "Her Majesty Victoria, by the Grace of God, of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland Queen, Defender of the Faith, Empress of India".[234]