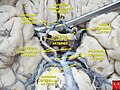
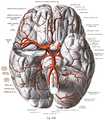
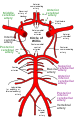
Anterior cerebral artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery.
Anterior cerebral artery
arteria cerebri anterior
Anterior cerebral artery syndrome refers to symptoms that follow a stroke occurring in the area normally supplied by one of the arteries. It is characterized by weakness and sensory loss in the lower leg and foot opposite to the lesion and behavioral changes.
Function[edit]
The anterior cerebral artery supplies a part of the frontal lobe, specifically its medial surface and the upper border. It also supplies the front four–fifths of the corpus callosum, and provides blood to deep structures such as the anterior limb of the internal capsule, part of the caudate nucleus, and the anterior part of the globus pallidus.[7]