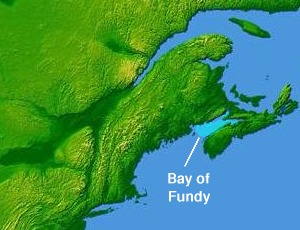
Bay of Fundy
The Bay of Fundy (French: Baie de Fundy) is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its tidal range is the highest in the world.[1] The name is probably a corruption of the French word fendu, meaning 'split'.[2]
For the local service district of Fundy Bay, see Saint George Parish, New Brunswick § Fundy Bay.Bay of Fundy
Estuary
Likely from the French Fendu, meaning "split".
Canada and USA
Atlantic Ocean
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--9DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
Geology[edit]
The story of the Fundy Basin begins about 200 million years ago in the early Jurassic, when all land on earth was part of a supercontinent called Pangaea. At that time what is now the Maritimes was situated near the equator and had a warm tropical climate and lush vegetation.[9] As continental drift reshaped the world, rift valleys formed, including the Cobequid–Chedabucto fault system.
During the continental breakup, magma erupted as basaltic lavas and left igneous rock formations such as the columnar jointing which can be seen on Brier and Grand Manan islands, among other places around the bay. These flows often are the sites of rarer mineral deposits including agate, amethyst, and stilbite, the latter being the provincial mineral of Nova Scotia.[9]
These rifts filled with sediment which became sedimentary rock. Many fossils have been found along the Fundy shoreline. The oldest dinosaur fossil in Canada was found at Burntcoat Head. Very early reptiles have been discovered in Carboniferous tree trunks at Joggins. Wasson Bluff has a rich trove of Jurassic fossils.
The bay is a member of the Global Geoparks Network,[10] a UNESCO initiative to promote and conserve the planet's geological heritage.
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#0__titleDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#0__subtitleDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#0__call_to_action.textDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#3__descriptionDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#2__titleDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#2__descriptionDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
Although some land areas are protected, there is no formal marine protection zone in the bay.[11] The Conservation Council of New Brunswick works to protect the ecosystem of the bay.[12][13] A result of shipping traffic has been the potential for increased collisions between ships and the critically endangered North Atlantic right whale. In 2003, the Canadian Coast Guard adjusted shipping lanes crossing prime whale feeding areas at the entrance to the Bay of Fundy to lessen the risk of collision. Many other marine mammals are found in the bay including fin whales, humpback whales, minke whales, Atlantic white-sided dolphin and the harbour porpoise.
The Bay of Fundy mudflats are a rare and unique intertidal habitat. Major mudflats are found on around the Maringouin Peninsula which lies between Shepody Bay and the Cumberland Basin and at the northern end of Chignecto Bay. On the Nova Scotia side, mudflats are found on the southern side of the Minas Basin and in Cobequid Bay. In the Minas Basin, the size of the mudflats from low to high water marks is as much as 4 km (2.5 mi).[14] Due to tidal turbulence, the water in these area contains very high amounts of fine sediment, source from tidal erosion of Carboniferous and Triassic sedimentary rock. Primary producers include hollow green weed, phytoplankton, algae, and sea lettuce.
Protected areas include:
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#4__titleDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#4__descriptionDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#3__titleDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__titleDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__subtextDEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--0DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--1DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--2DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--3DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--4DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--5DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--6DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--7DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$
$_$_$DEEZ_NUTS#1__answer--8DEEZ_NUTS$_$_$



