Chemistry
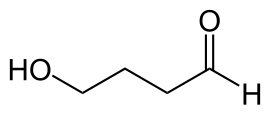
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter.[1] It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during reactions with other substances.[2][3][4][5] Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds.
For other uses, see Chemistry (disambiguation). "Chemical science" redirects here. For the journal, see Chemical Science (journal). Not to be confused with Kemistry.
In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology.[6] It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both basic and applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level.[7] For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the properties of the soil on the Moon (cosmochemistry), how medications work (pharmacology), and how to collect DNA evidence at a crime scene (forensics).
Chemistry has existed under various names since ancient times.[8] It has evolved, and now chemistry encompasses various areas of specialisation, or subdisciplines, that continue to increase in number and interrelate to create further interdisciplinary fields of study. The applications of various fields of chemistry are used frequently for economic purposes in the chemical industry.
Popular reading
Introductory undergraduate textbooks
Advanced undergraduate-level or graduate textbooks