Economic history of the United States
The economic history of the United States is about characteristics of and important developments in the economy of the U.S., from the colonial era to the present. The emphasis is on productivity and economic performance and how the economy was affected by new technologies, the change of size in economic sectors and the effects of legislation and government policy.
Further information: Technological and industrial history of the United StatesPre-colonial economy[edit]
Prior to the European conquest of North America, indigenous communities led a variety of economic lifestyles. Some were primarily agrarian whereas others prioritized hunting, gathering and foraging. While some early scholarship characterized these communities as non-market, more recent scholarship has made note of substantial and wide-ranging trade networks.[4]
In particular, much of the Mississippian drainage basin was characterized by settled agriculture and large towns in the pre-colonial period. According to a 2023 study, the plains were dominated by "organized, complex agricultural communities with settled populations that had opened and cleared land, domesticated plants, crafted irrigation systems, and determined the best rotation and fallow practices for a given region."[4]
Foreign vessels were excluded from carrying trade between ports within the British Empire
Manufactured goods from Europe to the colonies had to pass through England
Enumerated items, which included furs, ship masts, rice, indigo and tobacco, were only allowed to be exported to Great Britain.
Early 20th century[edit]
Economic growth and the 1910 break[edit]
The period from 1890 to 1910 was one of rapid economic growth of above 7%, in part due to rapid population growth. However, a sharp break in the growth rate to around 2.8% occurred from 1910 to 1929. Economists are uncertain what combination of supply and demand factors caused the break, but productivity growth was strong, enabling the labor cost per unit of output to decline from 1910 to 1929. The growth rate in hours worked fell 57% compared to the decline in the growth rate of output of 27%. It is generally accepted that the new technologies and more efficient business methods permanently shifted the supply and demand relationship for labor, with labor being in surplus (except during both world wars when the economy was engaged in war-time production and millions of men served in the armed forces). The technologies that became widespread after 1910, such as electrification, internal combustion powered transportation and mass production, were capital saving. Total non-residential business fixed capital spending fell after 1910 due to the fall of investment in structures.[253]
Great Depression and World War II: 1929–1945[edit]
Pre-war industry, commerce, and agriculture[edit]
Despite the Great Depression and World War II, the middle decades of the 20th century were among the highest for productivity growth.[278] [263] The research developed through informal cooperation between U.S. industry and academia grew rapidly and by the late 1930s exceeded the size of that taking place in Britain (although the quality of U.S. research was not yet on par with British and German research at the time).[279]
the collapse of the in 1971
Bretton Woods system
the growing influx of imported manufacturing goods, such as automobiles and electronics
the ,
1973 oil crisis
productivity growth fell to a low level after 1973 and remained low until the 1990s,
the 1973–1974 stock market crash,
and the ensuing displacement of by monetarist economics, especially by the free-market Chicago School of Economics, led by economist Milton Friedman. At the same time, the consensus among experts moved against New-Deal-style regulation, in favor of deregulation.
Keynesian economics
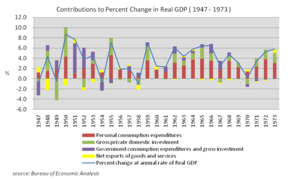
GDP per capita growth.
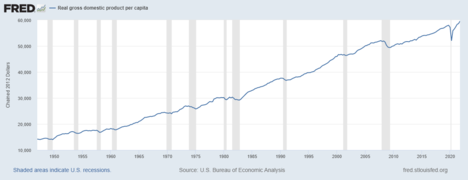
Real GDP per capita in the United States
Historical growth of the U.S. economy from 1961 to 2015
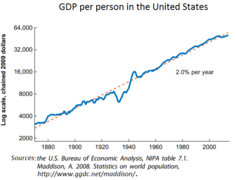
GDP per person in the United States
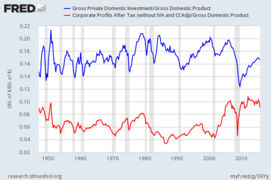
US Gross Private Domestic Investment and Corporate Profits After Tax as shares of Gross Domestic Product
US share of world GDP (%) since 1980.
US share of world GDP (nominal) peaked in 1985 with 32.74% of global GDP (nominal). The second-highest share was 32.24% in 2001.
US share of world GDP (PPP) peaked in 1999 with 23.78% of global GDP (PPP). The share has been declining each year since then.
U.S. in global economy
Atack, Jeremy; Passell, Peter (1994). . New York: W.W. Norton and Co. ISBN 978-0-393-96315-1. 1st edition was Lee, Susan Previant, and Peter Passell. A New Economic View of American History (1979) online 1st edition
A New Economic View of American History: From Colonial Times to 1940
Browning, Andrew H. The Panic of 1819: The First Great Depression (2019); scholarly history
excerpt
Cain, Louis P., Price V. Fishback and Paul W. Rhode, eds. The Oxford Handbook of American Economic History (2 vol Oxford Up, 2018) 961 pp.
online review
Carson, Thomas, ed. Gale Encyclopedia of U.S. Economic History (1999)
Chandler, Alfred D. The Visible Hand: The Management Revolution in American Business (1993)
online
Clark, Victor S. History of Manufacturers in the United States (3 vol. 1929); comprehensive coverage to the 1920s
online
Cochran, Thomas C. 200 Years of American Business. (1977)
online
Davis, Lance, Jonathan R. T. Hughes and Duncan M. McDougall. American Economic History: The Development Of A National Economy (2012)
DeLong, J. Bradford. Slouching Towards Utopia: An Economic History of the Twentieth Century (2022) global history with stress on USA.
Dubofsky, Melvyn, and Foster Rhea Dulles. Labor in America: A History (2004)
online older edition
Engerman, Stanley L. and Robert E. Gallman, eds. The Cambridge Economic History of the United States (2000), cover 1790–1914; heavily quantitative
Engerman, Stanley L.; Gallman, Robert E. (1996). . Cambridge Up. ISBN 978-0-521-39442-0. online
The Cambridge Economic History of the United States: vol 1: The Colonial Era
Faulkner, Harold U. The Decline of Laissez Faire, 1897–1917 (1951), broad survey of the era;
online
Faulkner, Harold U. Economic history of the United States (1937)
online
Fink, Leon. The long Gilded Age: American capitalism and the lessons of a new world order (University of Pennsylvania Press, 2014), short survey of late 19th century.
Fite, Emerson David. Social and industrial conditions in the North during the Civil War (1910) , old but still useful
online edition
French, Michael. US Economic History since 1945 (1997)
An Empire of Wealth: The Epic History of American Economic Power (2004), popular history
Gordon, John Steele
Gordon, Robert J. (2016). The Rise and Fall of American Growth. Princeton, NJ USA: Princeton University Press. 978-0-691-14772-7.
ISBN
Hughes, Jonathan and Louis P. Cain. American Economic History (8th Edition) (2010), textbook
Kirkland; Edward C. Industry Comes of Age: Business, Labor and Public Policy, 1860–1897 (1961), survey of era
Kirkland; Edward C. A History of American Economic Life (1951),
online
Lind, Michael. Land Of Promise: An Economic History of the United States (Harper, 2012).
and Russell R. Menard. The Economy of British America, 1607–1789 (1991)
McCusker, John J.
Matson, Cathy, ed. The Economy of Early America: Historical Perspectives and New Directions (2006)
excerpt and text search
Meyer, Balthasar Henry, and Caroline Elizabeth MacGill. History of Transportation in the United States before 1860 (1917). Archived January 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
online
Mitchell, Broadus. The Depression Decade: From New Era through New Deal, 1929–1941 (1947)
online
ed. The Oxford Encyclopedia of Economic History (5 vol. 2003), worldwide coverage by experts text search
Mokyr, Joel
Morris, Charles R. A Rabble of Dead Money: The Great Crash and the Global Depression: 1929–1939 (PublicAffairs, 2017), 389 pp.
online review
Myers, Margaret G. Financial History of the United States (1970).
online
Nettels, Curtis P. The Emergence of a National Economy, 1775–1815 (1962) broad economic history of the era
Nettels, Curtis P. Roots of American Civilization (1938), strong on colonial economics
online
Perkins, Edwin. The Economy of Colonial America (1988)
Porter, Glen. Encyclopedia of American Economic History: Studies of the Principal Movements and Ideas (3 vol 1980)
Rasmussen, Wayne D., ed. Agriculture in the United States: a documentary history (4 vol, Random House, 1975) 3661pp. ; primary sources
vol 4 online
Richardson, Heather Cox. The Greatest Nation of the Earth: Republican Economic Policies during the Civil War (1997)
Rosenberg, Nathan Inside the Black Box: Technology and Economics (1982)
Schapsmeier, Edward L; and Frederick H. Schapsmeier. Encyclopedia of American agricultural history (1975)
online
Shachtman, Tom. The Founding Fortunes: How the Wealthy Paid for and Profited from America's Revolution (St. Martin's Press, 2020) popular economic history covers 1763 and 1813;
online review
Schmidt, Louis Bernard, and Earle Dudley Ross, eds. Readings in the economic history of American agriculture (Macmillan, 1925) excerpts from scholarly studies, colonial era to 1920s. .
online
Sellers, Charles, The Market Revolution: Jacksonian America, 1815–1846 (1994)
excerpt
Siegler, Mark V. An Economic History of the United States: Connecting the Present with the Past (Macmillan, 2017), textbook with a topical approach
excerpt
Soule, George. The Prosperity Decade: From War to Depression, 1917–1929 (1947) broad economic history of decade;
online
Studenski, Paul, and Herman Krooss. A Financial History of the United States (2nd ed. 1963)
Taylor, George Rogers. The Transportation Revolution 1815–1860 (1962) broad economic history of the era;
online
Temin, Peter. The Jacksonian Economy (1969)
Walton, Gary M. and Hugh Rockoff. History of the American Economy with Economic Applications (2012), textbook
Whaples, Robert and Dianne C. Betts, eds. Historical Perspectives on the American Economy: Selected Readings (1995) articles
Woytinsky, V.S. World Population and Production: Trends and Outlook (1953). 1268 pp, tables, maps, analysis covering most industrial powers, 1800–1950; US is heavily represented;
online
Woytinsky, Emma S. Profile of the U.S. economy; a survey of growth and change (1967)
online
This article contains text from the United States Department of State from "State.gov". Archived from the original on August 31, 2006. Retrieved December 30, 2014.
public domain
Chandler, Alfred D. The Visible Hand: The Managerial Revolution in American Business (1977), business history
Chandler, Alfred D.; Strategy and Structure: Chapters in the History of the Industrial Enterprise (1969)
Chandler, Alfred D. and James W. Cortada. A Nation Transformed by Information: How Information Has Shaped the United States from Colonial Times to the Present
Chernow, Ron. The house of Morgan: an American banking dynasty and the rise of modern finance (2001).
Folsom, Burt, et al. The Myth of the Robber Barons (2010)
Gaspar, Vitor. "The making of a continental financial system: Lessons for Europe from early American history". Journal of European Integration 37.7 (2015): 847–859, summarizes Hamilton's achievements in Atlantic perspective.
Understanding the Gender Gap: An Economic History of American Women (1990), quantitative
Goldin, Claudia
Gordon, Robert. "U.S. Economic Growth since 1870: One Big Wave", American Economic Review 89:2 (May 1999), 123–28;
in JSTOR
Gordon, Robert. The Rise and Fall of American Growth: The U.S. Standard of Living since the Civil War (2016), Comprehensive coverage by leading scholar.
Klebaner, Benjamin J. American commercial banking: A history (Twayne, 1990).
online
La Barca, Giuseppe. International Trade under President Reagan: US Trade Policy in the 1980s (Bloomsbury, 2023). 978-1-350-27141-8
ISBN
Lindert, Peter H. and Jeffrey G. Williamson. Unequal Gains: American Growth and Inequality since 1700 (2016)
Link, Stefan J. Forging Global Fordism: Nazi Germany, Soviet Russia, and the Contest over the Industrial Order (2020)
excerpt
Mason, David L. From buildings and loans to bail-outs: A history of the American savings and loan industry, 1831–1995 (Cambridge University Press, 2004).
Misa, Thomas J. A Nation of Steel: The Making of Modern America, 1865–1925 (1995) , on steel industry
chapter 1 online
Morris, Charles R. The Tycoons: How Andrew Carnegie, John D. Rockefeller, Jay Gould, and J. P. Morgan Invented the American Supereconomy (2005)
Morris, Charles R. A Rabble of Dead Money: The Great Crash and the Global Depression: 1929–1939 (2017)
Murphy, Sharon Ann. Other People's Money: How Banking Worked in the Early American Republic (2017)
online review
Ransom, Roger. Conflict and Compromise: The Political Economy of Slavery, Emancipation and the American Civil War (1989)
Schweikart, Larry, ed. Banking and Finance to 1913 (1990); Banking and Finance, 1913–1989 (2 vol 1990), an encyclopedia with short articles by experts
Wright, Gavin. Old South, New South: Revolutions in the Southern Economy since the Civil War (1986)
Wright, Gavin. The Political Economy of the Cotton South: Households, Markets, and Wealth in the Nineteenth Century (1978)
Wright, Robert E. and David J. Cowen. Financial Founding Fathers: The Men Who Made America Rich, University of Chicago Press, 2006. 0-226-91068-7.
ISBN
Yarrow, Andrew L. "The big postwar story: Abundance and the rise of economic journalism". Journalism History 32.2 (2006): 58+
online
Bureau of the Census, Historical Statistics of the United States: Colonial Times to 1970 (1976) ; part 2 online; volumes 1 and 2
part 1 online
Carter, Susan B. et al. eds. The Historical Statistics of the United States (6 vol: Cambridge UP, 2006); huge compilation of statistical data;
online
complete series online; important analysis of current trends and policies, plus statistical tables
Council of Economic Advisors, Economic Report of the President (annual 1947– )
Bureau of Economic Analysis: Official United States GDP data
What Was the U.S. GDP Then? Annual Observations in Table and Graphical Format for years 1790 to Present.
Annual Report of the Secretary of the Treasury on the State of the Finances, 1789–1980
1863–1980
Annual Report of the Comptroller of the Currency
Annual Report of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
a graphic presentation of American financial history from 1861 through 1938
75 Years of American Finance
Statistical Abstract of the United States
Long Term Economic Growth – 1860–1965: A Statistical Compendium
a chart of the past trend of price inflation, federal debt, business, national income, stocks and bond yields for the United States from 1775 to 1943.
Business Booms and Depressions since 1775
Budget of the United States Government
594 historic photographs regarding American business and commerce; these are pre-1923 and out of copyright.
("Why your mental map of the US economy is probably wrong")