Heredity
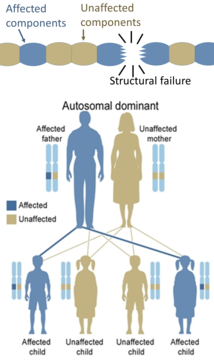
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics.
This article is about the transfer of characteristics from parent to offspring. For the academic journal, see Heredity (journal). For other uses, see Heredity (disambiguation).