Kingdom of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba (Latin: Scotia; Scottish Gaelic: Alba) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the First War of Scottish Independence.
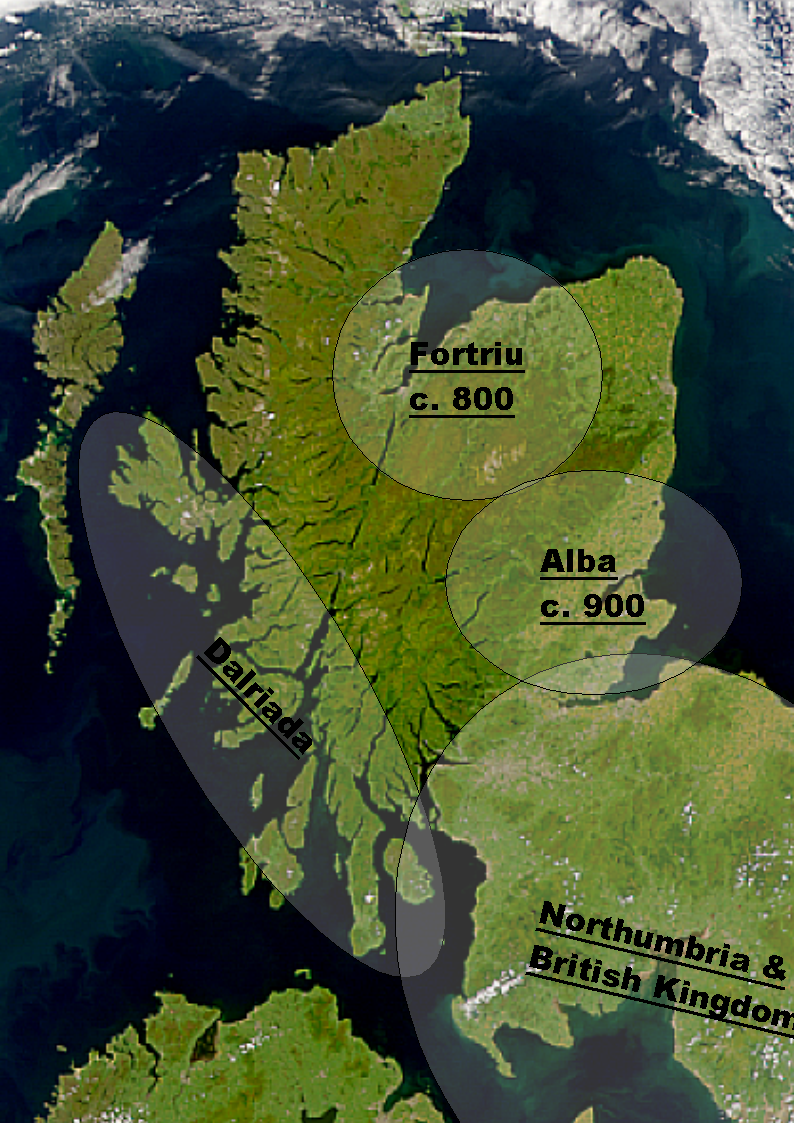
Alba included Dalriada, but initially excluded large parts of the present-day Scottish Lowlands, which were then divided between Strathclyde and Northumbria as far north as the Firth of Forth. Fortriu, a Pictish kingdom in the north, was added to Alba in the tenth century.
Until the early 13th century, Moray was not considered part of Alba, which was seen as extending only between the Firth of Forth and the River Spey.[1]
The name of Alba is one of convenience, as throughout this period both the ruling and lower classes of the kingdom were predominantly Pictish-Gaels, later Pictish-Gaels and Scoto-Normans. This differs markedly from the period of the House of Stuart, beginning in 1371, in which the ruling classes of the kingdom mostly spoke Middle English, which later evolved into and came to be called Lowland Scots. There is no precise Gaelic equivalent for the English term "Kingdom of Alba", as the Gaelic term Rìoghachd na h-Alba means 'Kingdom of Scotland'. English-speaking scholars adapted the Gaelic name for Scotland to apply to a particular political period in Scottish history, during the High Middle Ages.
Little is known about the structure of the Scottish royal court in the period before the coming of the Normans to Scotland, before the reign of David I. A little more is known about the court of the later 12th and 13th centuries. In the words of Geoffrey Barrow, this court "was emphatically feudal, Frankish, non-Celtic in character".[2] Some of the offices were Gaelic in origin, such as the Hostarius (later Usher or "Doorward"), the man in charge of the royal bodyguard, and the rannaire, the Gaelic-speaking member of the court whose job was to divide the food.[3]
In the 13th century, all the other offices tended to be hereditary, with the exception of the Chancellor. The royal household of course came with numerous other offices. The most important was probably the aforementioned hostarius, but there were others such as the royal hunters, the royal foresters and the cooks (dispensa or spence).