Mantoux test
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening for tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis diagnosis. It is one of the major tuberculin skin tests used around the world, largely replacing multiple-puncture tests such as the tine test. The Heaf test, a form of tine test, was used until 2005 in the UK, when it was replaced by the Mantoux test. The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It was also used in the USSR and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states, although Soviet mantoux produced many false positives due to children's allergic reaction.[1]
Mantoux test
Mantoux screening test
screen for tuberculosis
Procedure[edit]
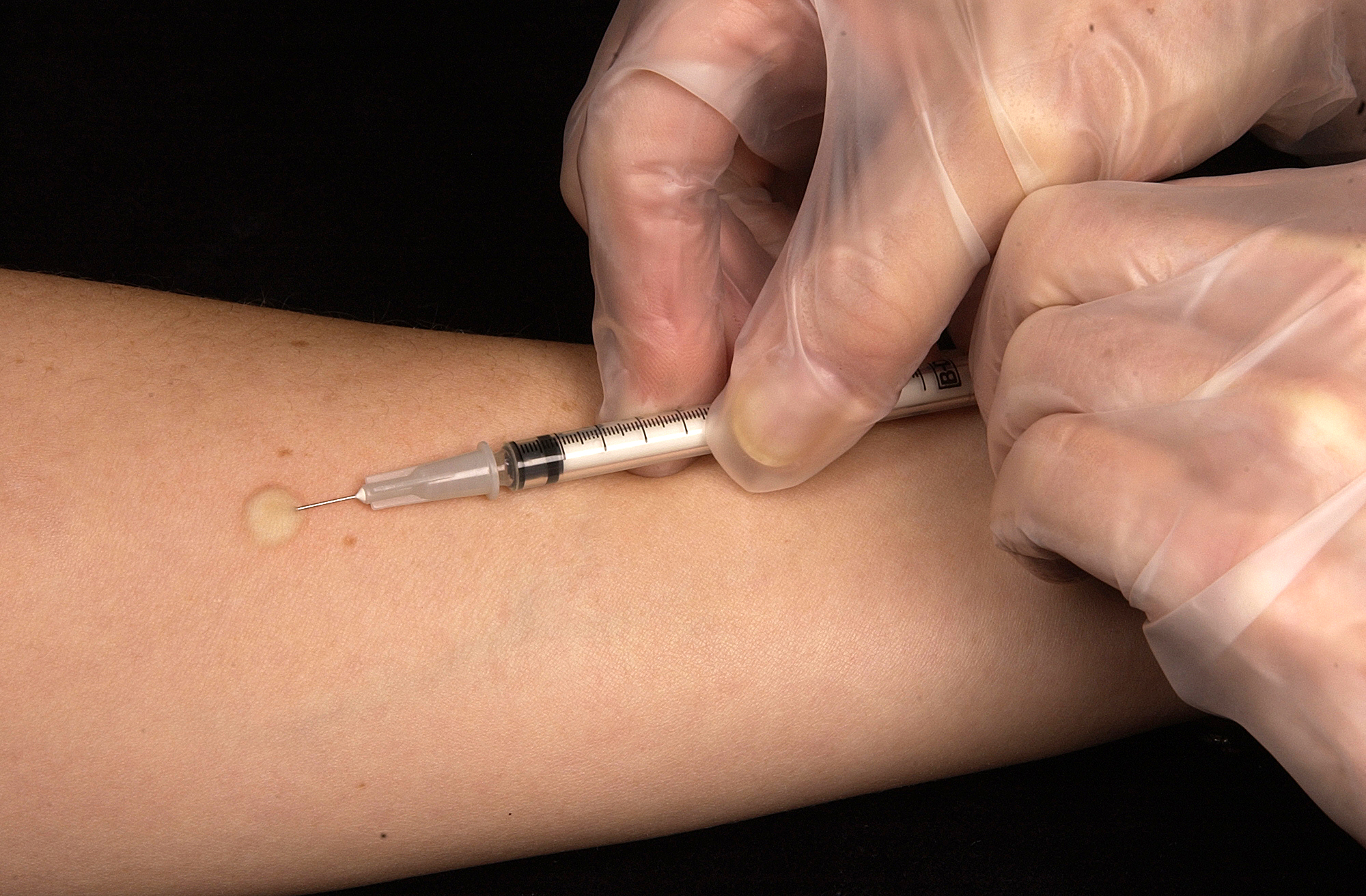
In the Mantoux test, a standard dose of 5 tuberculin units (TU - 0.1 ml), according to the CDC,[8] or 2 TU of Statens Serum Institute (SSI) tuberculin RT23 in 0.1 ml solution, according to the National Health Service,[9] is injected intradermally (between the layers of dermis) on the flexor surface of the left forearm, mid-way between elbow and wrist. The injection should be made with a tuberculin syringe, with the needle bevel facing upward. When placed correctly, injection should produce a pale wheal of the skin, 6 to 10 mm in diameter. The result of the test is read after 48–96 hours but 72 hours (3rd day) is the ideal. This intradermal injection is termed the Mantoux technique. A person who has been exposed to the bacteria is expected to mount an immune response in the skin containing the bacterial proteins. The response is a classical example of delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction (DTH), a type IV of hypersensitivities. T cells and myeloid cells are attracted to the site of reaction in 1–3 days and generate local inflammation. The reaction is read by measuring the diameter of induration (palpable raised, hardened area) across the forearm (perpendicular to the long axis) in millimeters. If there is no induration, the result should be recorded as "0 mm". Erythema (redness) should not be measured.[10] In the Pirquet version of the test tuberculin is applied to the skin via scarification.[11]
The results of this test must be interpreted carefully. The person's medical risk factors determine at which increment (5 mm, 10 mm, or 15 mm) of induration the result is considered positive.[12] A positive result indicates TB exposure.
A tuberculin test conversion is defined as an increase of 10 mm or more within a two-year period, regardless of age. Alternative criteria include increases of 6, 12, 15 or 18 mm.[14]
False positive result[edit]
TST (tuberculin skin test) positive is measured by size of induration. The size of the induration considered to be a positive result depends on risk factors. For example, a low-risk patient must have a larger induration for a positive result than a high-risk patient. High-risk groups include recent contacts, those with HIV, those with chest radiograph with fibrotic changes, organ transplant recipients, and those with immunosuppression.
According to the Ohio Department of Health and US Department of Health, the Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine does not protect against TB infection. It does, though, give 80% of children protection against tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis. Therefore, a positive TST/PPD in a person who has received BCG vaccine is interpreted as latent TB infection (LTBI).[15]
Due to the test's low specificity, most positive reactions in low-risk individuals are false positives.[16] A false positive result may be caused by nontuberculous mycobacteria or previous administration of BCG vaccine. Vaccination with BCG may result in a false-positive result for many years after vaccination.[17]
False positives can also occur when the injected area is touched, causing swelling and itching. If the swelling is less than 5 mm, it is possibly due to error by the healthcare personnel causing inflammation to the area.
Another source of false positive results can be allergic reaction or hypersensitivity. Although rare (about 0.08 reported reactions per million doses of tuberculin), these reactions can be dangerous and precautions should be taken by having epinephrin available.[18]
Reaction to the PPD or tuberculin test is suppressed by the following conditions:
This is because the immune system needs to be functional to mount a response to the protein derivative injected under the skin. A false negative result may occur in a person who has been recently infected with TB, but whose immune system hasn't yet reacted to the bacteria.
In case a second tuberculin test is necessary it should be carried out in the other arm to avoid hypersensitising the skin.
The role of Mantoux testing in people who have been vaccinated is disputed. The US recommends that tuberculin skin testing is not contraindicated for BCG-vaccinated persons, and prior BCG vaccination should not influence the interpretation of the test. The UK recommends that interferon-γ testing should be used to help interpret positive Mantoux tests of over 5 mm,[19] and repeated tuberculin skin testing must not be done in people who have had BCG vaccinations. In general, the US recommendation may result in a larger number of people being falsely diagnosed with latent tuberculosis, while the UK approach has an increased chance of missing patients with latent tuberculosis who should be treated.
According to the US guidelines, latent tuberculosis infection diagnosis and treatment is considered for any BCG-vaccinated person whose skin test is 10 mm or greater, if any of these circumstances are present:
Anergy testing[edit]
In cases of anergy, a lack of reaction by the body's defence mechanisms when it comes into contact with foreign substances, the tuberculin reaction will occur weakly, thus compromising the value of Mantoux testing. For example, anergy is present in AIDS, a disease which strongly depresses the immune system. Therefore, anergy testing is advised in cases where there is suspicion that anergy is present. However, routine anergy skin testing is not recommended.[20]
Some people who have been infected with TB may have a negative reaction when tested years after infection, as the immune system response may gradually wane. This initial skin test, though negative, may stimulate (boost) the body's ability to react to tuberculin in future tests. Thus, a positive reaction to a subsequent test may be misinterpreted as a new infection, when in fact it is the result of the boosted reaction to an old infection.[21]
Use of two-step testing is recommended for initial skin testing of adults who will be retested periodically (e.g., health care workers). This ensures any future positive tests can be interpreted as being caused by a new infection, rather than simply a reaction to an old infection.
A person who is diagnosed as "infected in the distant past" on two-step testing is called a "tuberculin reactor".
The US recommendation that prior BCG vaccination be ignored results in almost universal false diagnosis of tuberculosis infection in people who have had BCG (mostly foreign nationals).
According to the guidelines published by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2005, the results are re-categorized into 3 parts based on their previous or baseline outcomes:
Recent developments[edit]
In addition to tuberculin skin tests such as (principally) the Mantoux test, interferon gamma release assays (IGRAs) have become common in clinical use in the 2010s. In some contexts they are used instead of TSTs, whereas in other contexts TSTs and IGRAs both continue to be useful.[24]
The QuantiFERON-TB Gold blood test measures the patient's immune reactivity to the TB bacterium, and is useful for initial and serial testing of persons with an increased risk of latent or active tuberculosis infection. Guidelines for its use were released by the CDC in December 2005.[25] QuantiFERON-TB Gold is FDA-approved in the United States, has CE Mark approval in Europe and has been approved by the MHLW in Japan. The interferon gamma release assay is the preferred method for patients who have had immunosuppression and are about to start biological therapies.[26]
T-SPOT.TB is another IGRA; it uses the ELISPOT method.
The Heaf tuberculin skin test was used in the United Kingdom, but discontinued in 2005. The equivalent Mantoux test positive levels done with 10 TU (0.1 ml at 100 TU/ml, 1:1000) are