Mongol invasions and conquests
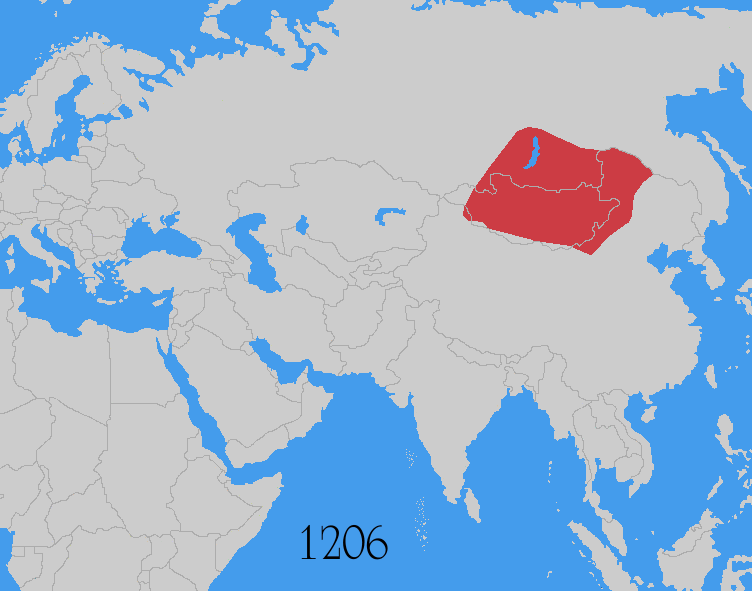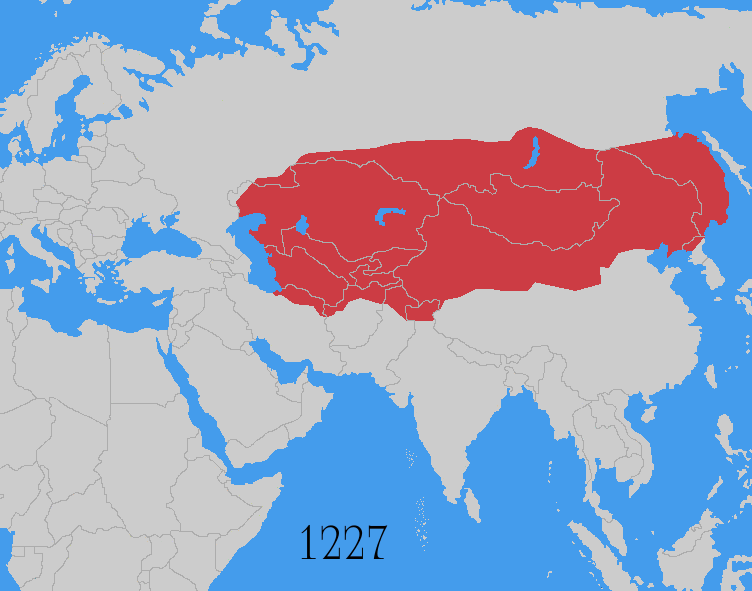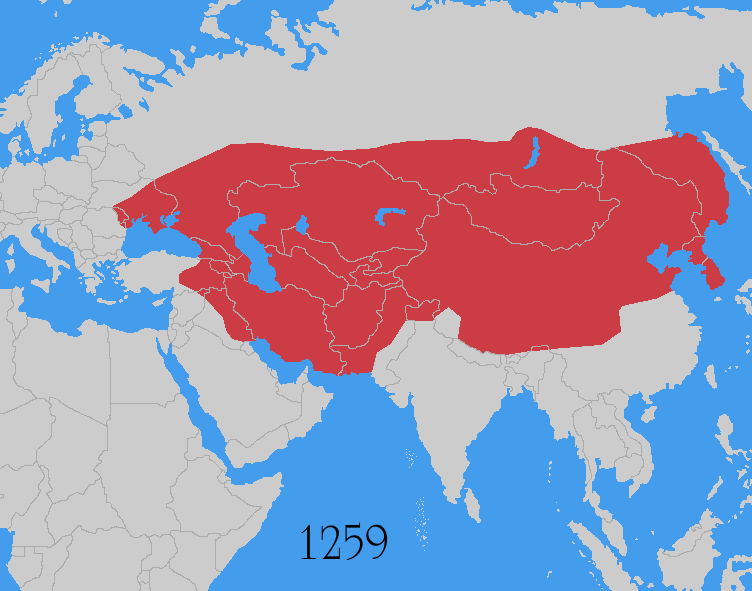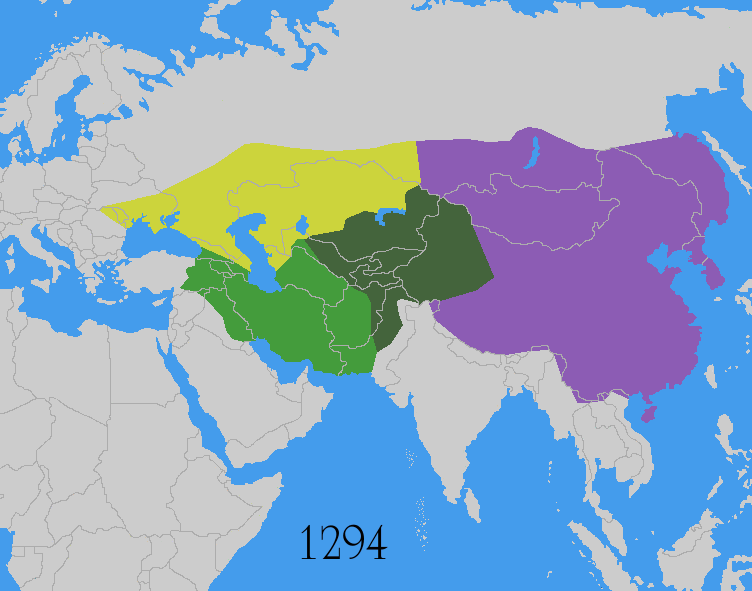
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire, the Mongol Empire (1206–1368), which by 1260 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history.[4][5]
Overview[edit]
The Mongol Empire developed in the course of the 13th century through a series of victorious campaigns throughout Eurasia. At its height, it stretched from the Pacific to Central Europe. In contrast with later "empires of the sea" such as the European colonial powers, the Mongol Empire was a land power, fueled by the grass-foraging Mongol cavalry and cattle.[a] Thus most Mongol conquest and plundering took place during the warmer seasons, when there was sufficient grazing for their herds.[6] The rise of the Mongols was preceded by 15 years of wet and warm weather conditions from 1211 to 1225 that allowed favourable conditions for the breeding of horses, which greatly assisted their expansion.[7]
As the Mongol Empire began to fragment from 1260, conflict between the Mongols and Eastern European polities continued for centuries. Mongols continued to rule China into the 14th century under the Yuan dynasty, while Mongol rule in Persia persisted into the 15th century under the Timurid Empire. In India, the later Mughal Empire survived into the 19th century.