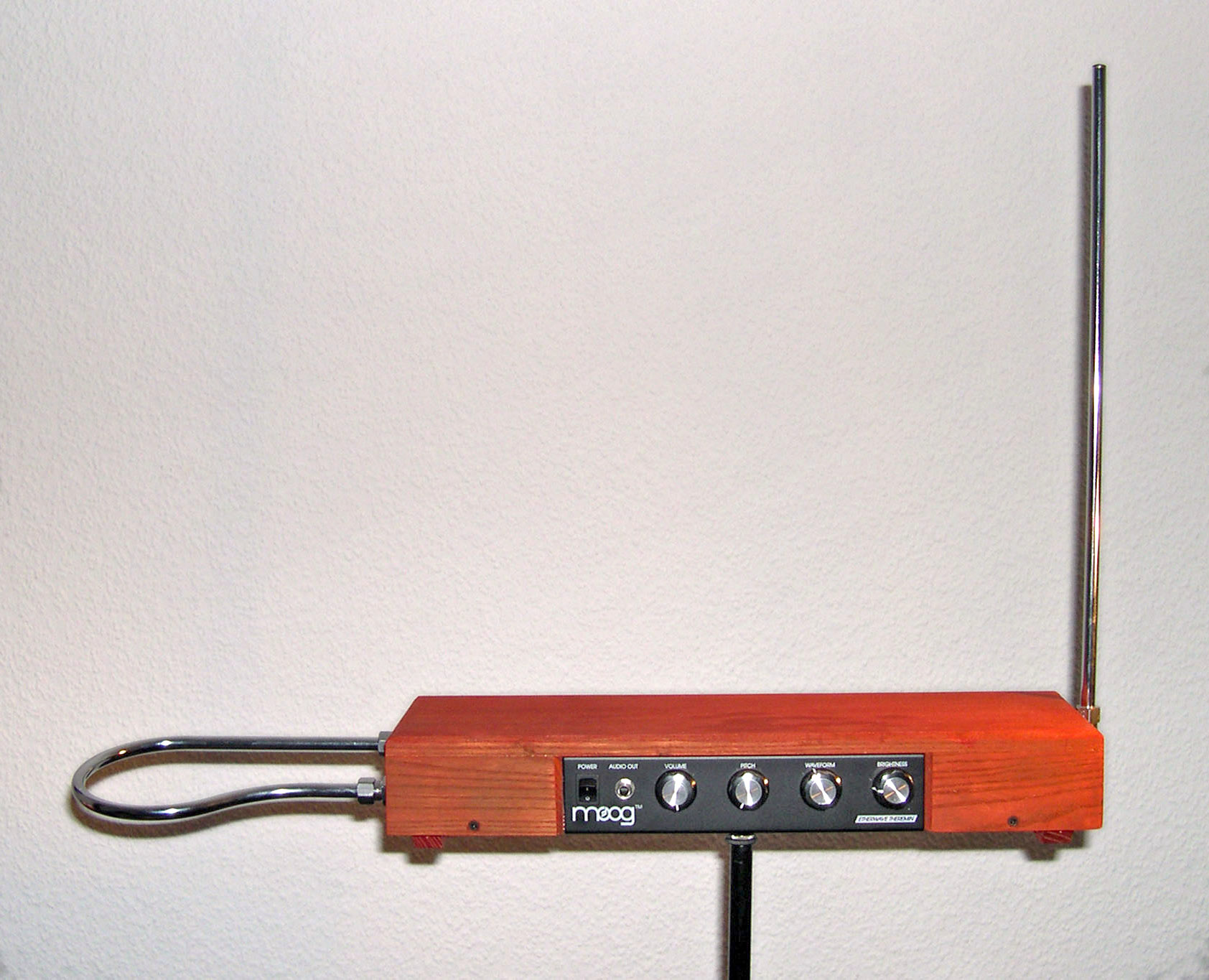
Theremin
The theremin (/ˈθɛrəmɪn/; originally known as the ætherphone, etherphone, thereminophone[2] or termenvox/ thereminvox) is an electronic musical instrument controlled without physical contact by the performer (who is known as a thereminist). It is named after its inventor, Leon Theremin, who patented the device in 1928.
This article is about the electronic musical instrument. For its inventor, see Leon Theremin. For the Covenant album, see Theremin (album).
The instrument's controlling section usually consists of two metal antennas which function not as radio antennas but rather as position sensors. Each antenna forms one half of a capacitor with each of the thereminist's hands as the other half of the capacitor. These antennas capacitively sense the relative position of the hands and control oscillators for frequency with one hand, and amplitude (volume) with the other. The electric signals from the theremin are amplified and sent to a loudspeaker.
The sound of the instrument is often associated with eerie situations. The theremin has been used in movie soundtracks such as Miklós Rózsa's Spellbound and The Lost Weekend, Bernard Herrmann's The Day the Earth Stood Still, and Justin Hurwitz's First Man, as well as in theme songs for television shows such as the ITV drama Midsomer Murders and the Disney+ series Loki, the latter composed by Natalie Holt. The theremin is also used in concert music (especially avant-garde and 20th- and 21st-century new music); for example, Mano Divina Giannone is a popular American thereminist who along with his orchestra, The Divine Hand Ensemble, regularly holds said concerts. It is also used in popular music genres, such as rock.