British occupation zone in Germany
The British occupation zone in Germany (German: Britische Besatzungszone Deutschlands) was one of the Allied-occupied areas in Germany after World War II. The United Kingdom, along with the Commonwealth, was one of the three major Allied powers that defeated Nazi Germany. By 1945, the Allies had divided the country into four occupation zones: British, Soviet, American and French lasting until 1949, whence the new country of West Germany was established. Out of all the four zones, the British had the largest population and contained within it the heavy industry region, the Ruhr, as well as the naval ports and Germany's coast lines.
British occupation zone in GermanyBritische Besatzungszone Deutschlands
Cold War
8 May 1945
5 July 1945
7 October 1949
12 September 1990
Background[edit]
By the end of 1942, Britain was already thinking about post war strategy, and in particular the occupation of Germany. This became more of a reality when the British Liberation Army consisting largely of the 21st Army Group had landed in Normandy on 6 June 1944. Having fought all the way into Northern France and the Low Countries they had reached the German borders by the end of the year.
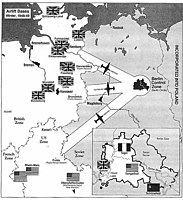
Meanwhile, the 'Big Three' - Winston Churchill, Franklin D. Roosevelt and Joseph Stalin met at the Yalta Conference between 4 and 11 February 1945 to discuss Germany's post-war occupation, which included coming to a final determination of the inter-zonal borders. The three powers divided "Germany as a whole" into four occupation zones for administrative purposes under the three Western Allies the United States, the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union, respectively. This division was ratified at the August 1945 Potsdam Conference.[1] This set aside an earlier division into three zones (excluding France) proposed by the September 1944 London Protocol. Stalin agreed that France would have a fourth occupation zone in Germany and this was formed from the American and the British zones.
In the final offensive the First Canadian Army wheeled left and liberated the northern part of the Netherlands and captured adjoining areas of Germany, the British Second Army swept into and occupied much of north-west Germany.[2] The liberation of the concentration camps such as Bergen Belsen put the strategy of post war Germany into a new direction. This meant that denazification was put at the forefront of British post war policy in Germany.
On 4 May 1945, Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery accepted the unconditional surrender of the German forces in the Netherlands, in north west Germany and Denmark. This was followed by the German Instrument of Surrender three days later.[3]
For the French zone the Americans ceded their part - land south of Baden-Baden, land south of the Free People's State of Württemberg (which became Württemberg-Hohenzollern), the Lindau region on Lake Constance, and four regions in Hesse east of the Rhine. The British ceded the Saarland, the Palatinate, and territories on the left bank of the Rhine to Remagen (including Trier, Koblenz, and Montabaur). Also created was the Inner German Border as the boundary between the Western and Soviet occupation zones.