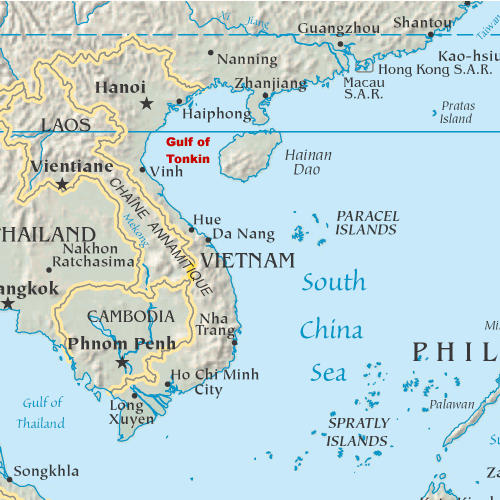
Gulf of Tonkin
The Gulf of Tonkin is a gulf at the northwestern portion of the South China Sea, located off the coasts of Tonkin (northern Vietnam) and South China. It has a total surface area of 126,250 km2 (48,750 sq mi). It is defined in the west and northwest by the northern coastline of Vietnam down to the Hòn La Island, in the north by China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, and to the east by the Leizhou Peninsula and Hainan Island.
This article is about the body of water. For the 1964 military incident, see Gulf of Tonkin incident. For the American political resolution, see Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. For the economic zone, see Gulf of Tonkin Economic Belt.Gulf of Tonkin
北部灣
東京灣
北部湾
东京湾
Northern Gulf
Gulf of Tonkin
Běibù Wān
Dōngjīng Wān
Běibù Wān
Dōngjīng Wān
Bak1 bou6 waan1
Dung1 ging1 waan1
Pak-pōe oân
Tang-kiann oân
Vịnh Bắc Bộ
Vịnh Bắc Phần
Vịnh Đông Kinh
Vịnh Bắc Việt
泳北部
泳北份
泳東京
泳北越
Description and etymology[edit]
The name Tonkin, written "東京" in chữ Hán characters and Đông Kinh in the Vietnamese alphabet, means "eastern capital", and is the former toponym for Hanoi, the present capital of Vietnam. It is not to be confused with Tokyo, which is also written "東京" and also means "eastern capital". During the French colonial era, the northern region of today’s Vietnam was called Tonkin.
Bắc Bộ is the native Vietnamese name of Tonkin. The bay's Vietnamese and Chinese names – Vịnh Bắc Bộ and Běibù Wān, respectively – both mean "Northern Bay".
The Gulf of Tonkin is a relatively shallow portion of the Pacific Ocean; the majority of the gulf's ocean floor is less than 75 metres (246 ft) in depth, and no part of the gulf is submerged in more than 100 metres (330 ft) of water.[1]