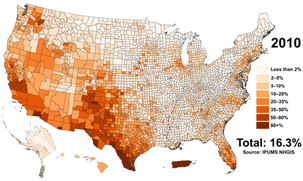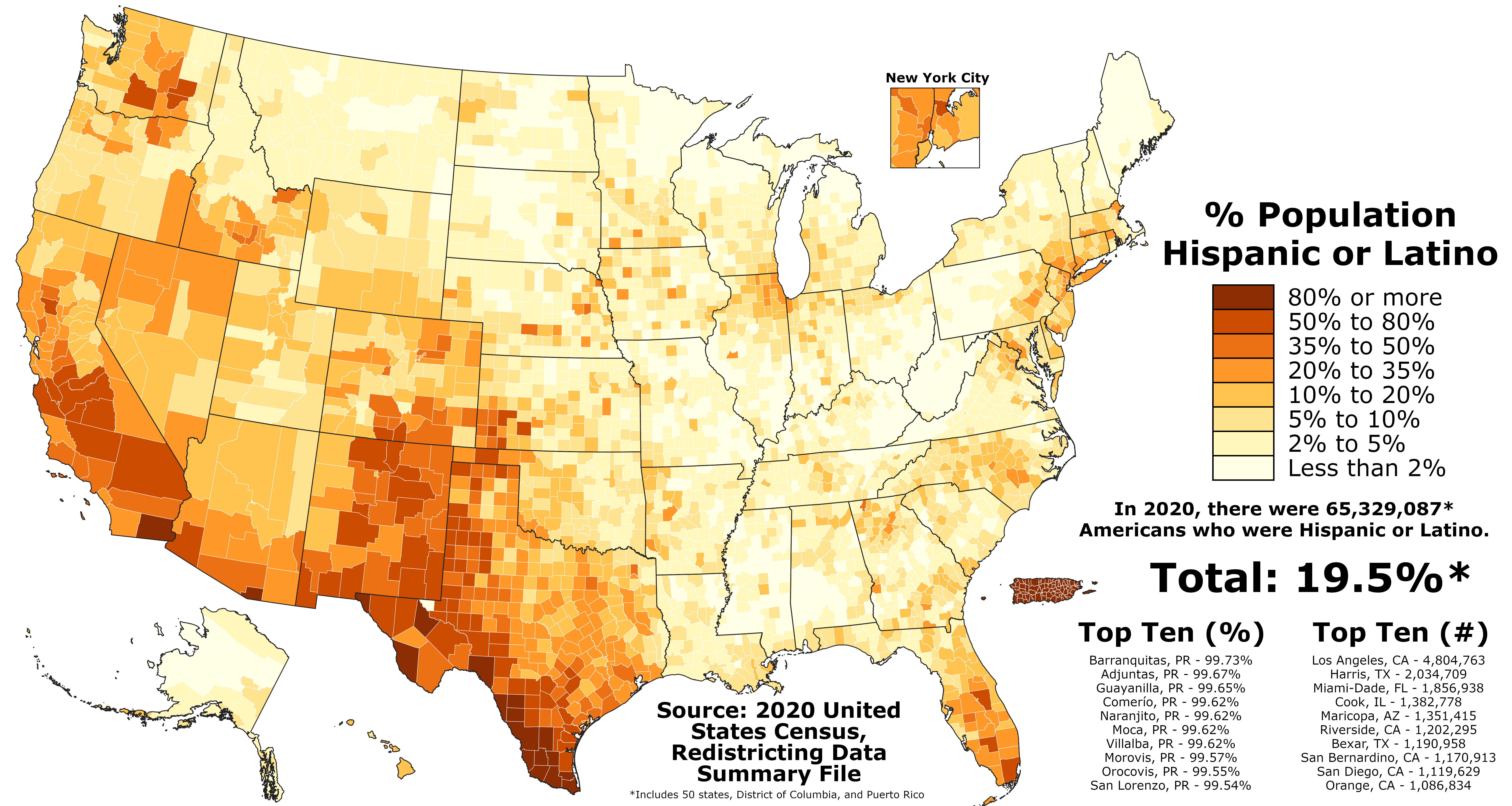
Hispanic and Latino Americans
Hispanic and Latino Americans (Spanish: Estadounidenses hispanos y latinos; Portuguese: Estadunidenses hispânicos e latinos) are Americans of full or partial Spanish and/or Latin American background, culture, or family origin.[3][4][5][6] These demographics include all Americans who identify as Hispanic or Latino regardless of race.[7][8][9][10][11][12] As of 2020, the Census Bureau estimated that there were almost 65.3 million Hispanics and Latinos living in the United States and its territories.
"Hispanic and Latino" redirects here. For the ethnic categories, see Hispanic and Latino (ethnic categories).
"Origin" can be viewed as the ancestry, nationality group, lineage or country of birth of the person or the person's parents or ancestors before their arrival in the United States of America. People who identify as Hispanic or Latino may be of any race, because similar to what occurred during the colonization and post-independence of the United States, Latin American countries had their populations made up of descendants of white European colonizers (in this case Portuguese and Spaniards), Native peoples of the Americas, descendants of African slaves, post-independence immigrants coming from Europe, Middle East and East Asia, as well as descendants of multiracial unions between these different ethnic groups.[13][14][15][16] As one of the only two specifically designated categories of ethnicity in the United States, Hispanics and Latinos form a pan-ethnicity incorporating a diversity of inter-related cultural and linguistic heritages, the use of the Spanish and Portuguese languages being the most important of all. Most Hispanic and Latino Americans are of Mexican, Puerto Rican, Cuban, Salvadoran, Dominican, Colombian, Guatemalan, Honduran, Ecuadorian, Peruvian, Venezuelan or Nicaraguan origin. The predominant origin of regional Hispanic and Latino populations varies widely in different locations across the country.[14][17][18][19][20] In 2012, Hispanic Americans were the second fastest-growing ethnic group by percentage growth in the United States after Asian Americans.[21]
Multiracial Hispanics (Mestizo) of Indigenous descent and Spanish descent are the second oldest ethnic groups (after the Native Americans) to inhabit much of what is today the United States.[22][23][24][25] Spain colonized large areas of what is today the American Southwest and West Coast, as well as Florida. Its holdings included present-day California, Texas, New Mexico, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and Florida, all of which constituted part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, based in Mexico City. Later, this vast territory became part of Mexico after its independence from Spain in 1821 and until the end of the Mexican–American War in 1848. Hispanic immigrants to the New York/New Jersey metropolitan area derive from a broad spectrum of Hispanic countries.[26]
Places of settlement in United States:
Diaspora:
Individuals:
Other Hispanic and Latino Americans topics:
General: