Perea
Perea or Peraea (Greek: Περαία, "the country beyond") was the term used mainly during the early Roman period for part of ancient Transjordan. It lay broadly east of Judea and Samaria, which were situated on the western side of the Jordan River, and southwest of the Decapolis.
For the surname, see Perea (surname).Perea was part of the kingdom of Herod the Great and his descendants, and later of subsequent Roman provinces that included Iudaea.
Geography[edit]
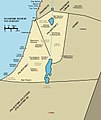
Perea was a slender piece of land east of the Jordan River. It stretched from Wadi Yabis in the north to Wadi Mujib (Nahal Arnon) in the south. The region extended from the Jordan River westwards to the foothills eastward towards Amman (then known as Philadelphia). Josephus notes that Perea's northern boundary was near Pella, while to the east, it bordered the territories of Gerasa and Philadelphia (both part of the Decapolis) and Heshbon. To the south, it was adjacent to the Land of Moab, with Machaerus marking its southernmost fortress.[1]
Encompassing roughly 2,625 square kilometers, Josephus was accurate in stating that Perea surpassed Galilee in size, as Galilee spanned approximately 2,200 square kilometers. Josephus depicted Perea mainly as "desert" and "rugged," with pockets of well-cultivated areas, a feature now undergoing transformation due to extensive irrigation initiatives.[2]
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Wood, James, ed. (1907). "Perea". The Nuttall Encyclopædia. London and New York: Frederick Warne.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Wood, James, ed. (1907). "Perea". The Nuttall Encyclopædia. London and New York: Frederick Warne.