Thoracic aorta
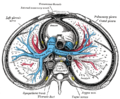
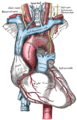
The thoracic aorta is a part of the aorta located in the thorax. It is a continuation of the aortic arch. It is located within the posterior mediastinal cavity, but frequently bulges into the left pleural cavity. The descending thoracic aorta begins at the lower border of the fourth thoracic vertebra and ends in front of the lower border of the twelfth thoracic vertebra, at the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm where it becomes the abdominal aorta.
Thoracic aorta
At its commencement, it is situated on the left of the vertebral column; it approaches the median line as it descends; and, at its termination, lies directly in front of the column.
The thoracic aorta has a curved shape that faces forward, and has small branches. It has a radius of approximately 1.16 cm.[1]
The aorta is an artery that conveys oxygenated blood from the heart to other parts of the body. It is one of the largest arteries in the body.[2] The aorta gives off several paired branches as it descends. In descending order, these include the
Note: The posterior intercostal arteries are branches that originate throughout the length of the posterior aspect of the descending thoracic aorta.