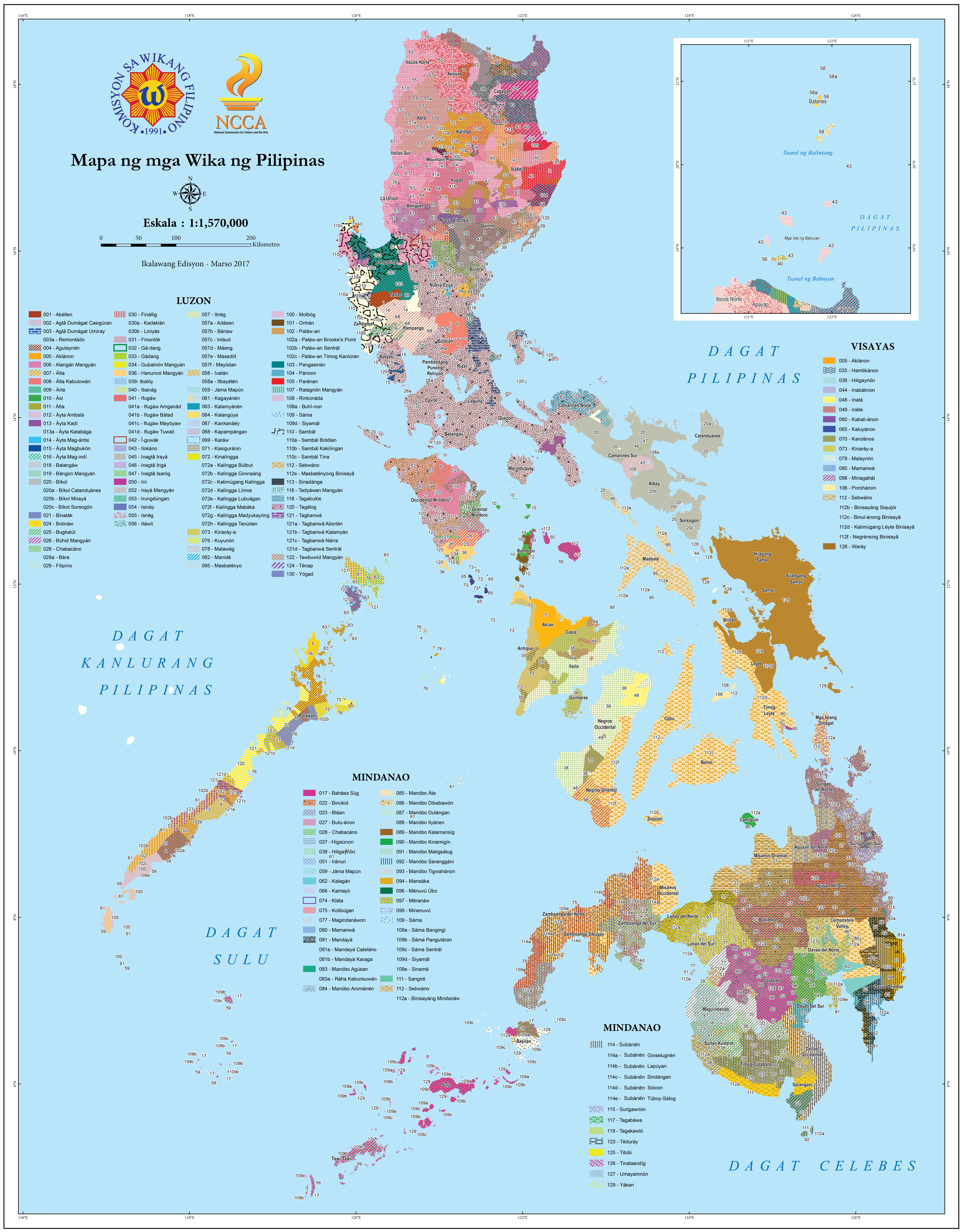
Languages of the Philippines
There are some 130 to 195 languages spoken in the Philippines, depending on the method of classification.[3][4][5][6] Almost all are Malayo-Polynesian languages native to the archipelago. A number of Spanish-influenced creole varieties generally called Chavacano along with some local varieties of Chinese[7][8][9] are also spoken in certain communities. The 1987 constitution designates Filipino, a standardized version of Tagalog, as the national language and an official language along with English. Filipino is regulated by Commission on the Filipino Language and serves as a lingua franca used by Filipinos of various ethnolinguistic backgrounds.[10]
Languages of the Philippines
Republic Act 11106 declares Filipino Sign Language or FSL as the country's official sign language and as the Philippine government's official language in communicating with the Filipino Deaf.[11]
While Filipino is used for communication across the country's diverse linguistic groups and in popular culture, the government operates mostly using English. Including second-language speakers, there are more speakers of Filipino than English in the Philippines.[12] The other regional languages are given official auxiliary status in their respective places according to the constitution but particular languages are not specified.[13] Some of these regional languages are also used in education.[2]
The indigenous scripts of the Philippines (such as the Kulitan, Tagbanwa and others) are used very little; instead, Philippine languages are today written in the Latin script because of the Spanish and American colonial experience. Baybayin, though generally not understood, is one of the most well-known of the Philippine indigenous scripts and is used mainly in artistic applications such as on current Philippine banknotes, where the word "Pilipino" is inscribed using the writing system. Additionally, the Arabic script is used in the Muslim areas in the southern Philippines.
Tagalog and Cebuano are the most commonly spoken native languages, together comprising about half of the population of the Philippines. Filipino and English are the only official languages and are taught in schools. This, among other reasons, has resulted in a rivalry between the Tagalog and Cebuano language groups.[14]
Language vitality[edit]
2010 UNESCO designation[edit]
Endangered and extinct languages in the Philippines are based on the 3rd world volume released by UNESCO in 2010.
Degree of endangerment (UNESCO standard)
Major immigrant languages[edit]
Arabic[edit]
Arabic is used by some Filipino Muslims in both a liturgical and instructional capacity since the arrival of Islam and establishment of several Sultanates in the 14th century. Along with Malay, Arabic was the lingua franca of the Malay Archipelago among Muslim traders and the Malay aristocracy.
The 1987 Constitution mandates that Arabic (along with Spanish) is to be promoted on an optional and voluntary basis. As of 2015 Arabic is taught for free and is promoted in some Islamic centres predominantly in the southernmost parts of Philippines. It is used primarily in religious activities and education (such as in a madrasa or Islamic school) and rarely for official events or daily conversation. In this respect, its function and use is somewhat like the traditional roles of Latin and Spanish in Filipino Catholicism vis-à-vis other currently spoken languages.
Islamic schools in Mindanao teach Modern Standard Arabic in their curriculum.[51]
