Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire (Portuguese: Império Português, European Portuguese: [ĩˈpɛ.ɾju puɾ.tuˈɣeʃ]), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (Ultramar Português) or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (Império Colonial Português), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and later overseas territories, governed by the Kingdom of Portugal. It was one of the longest-lived colonial empires in European history, lasting 584 years from the conquest of Ceuta in North Africa in 1415, to the transfer of sovereignty over Macau to China in 1999. The empire began in the 15th century, and from the early 16th century it stretched across the globe, with bases in Africa, North America, South America, and various regions of Asia and Oceania.[1][2][3]
Portuguese EmpireImpério Português
Lisbon
(1415–1999)
1415
1498
1500
1580–1640
1588–1654
1640–1668
1769
1822
1961
1961–1974
1974–1975
1999
The Portuguese Empire originated at the beginning of the Age of Discovery, and the power and influence of the Kingdom of Portugal would eventually expand across the globe. In the wake of the Reconquista, Portuguese sailors began exploring the coast of Africa and the Atlantic archipelagos in 1418–1419, using recent developments in navigation, cartography, and maritime technology such as the caravel, with the aim of finding a sea route to the source of the lucrative spice trade. In 1488, Bartolomeu Dias rounded the Cape of Good Hope, and in 1498 Vasco da Gama reached India. In 1500, either by an accidental landfall or by the crown's secret design, Pedro Álvares Cabral reached what would be Brazil.
Over the following decades, Portuguese sailors continued to explore the coasts and islands of East Asia, establishing forts and factories as they went. By 1571, a string of naval outposts connected Lisbon to Nagasaki along the coasts of Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia. This commercial network and the colonial trade had a substantial positive impact on Portuguese economic growth (1500–1800) when it accounted for about a fifth of Portugal's per-capita income.
When King Philip II of Spain (Philip I of Portugal) seized the Portuguese crown in 1580, there began a 60-year union between Spain and Portugal known to subsequent historiography as the Iberian Union, although the realms continued to have separate administrations. As the King of Spain was also King of Portugal, Portuguese colonies became the subject of attacks by three rival European powers hostile to Spain: the Dutch Republic, England, and France. With its smaller population, Portugal found itself unable to effectively defend its overstretched network of trading posts, and the empire began a long and gradual decline. Eventually, Brazil became the most valuable colony of the second era of empire (1663–1825), until, as part of the wave of independence movements that swept the Americas during the early 19th century, it broke away in 1822.
The third era of empire covers the final stage of Portuguese colonialism after the independence of Brazil in the 1820s. By then, the colonial possessions had been reduced to forts and plantations along the African coastline (expanded inland during the Scramble for Africa in the late 19th century), Portuguese Timor, and enclaves in India (Portuguese India) and China (Portuguese Macau). The 1890 British Ultimatum led to the contraction of Portuguese ambitions in Africa.
Under António Salazar (in office 1932–1968), the Estado Novo dictatorship made some ill-fated attempts to cling on to its last remaining colonies. Under the ideology of pluricontinentalism, the regime renamed its colonies "overseas provinces" while retaining the system of forced labour, from which only a small indigenous élite was normally exempt. In August 1961, the Dahomey annexed the Fort of São João Baptista de Ajudá, and in December that year India annexed Goa, Daman, and Diu. The Portuguese Colonial War in Africa lasted from 1961 until the final overthrow of the Estado Novo regime in 1974. The Carnation Revolution of April 1974 in Lisbon led to the hasty decolonization of Portuguese Africa and to the 1975 annexation of Portuguese Timor by Indonesia. Decolonization prompted the exodus of nearly all the Portuguese colonial settlers and of many mixed-race people from the colonies. Portugal returned Macau to China in 1999. The only overseas possessions to remain under Portuguese rule, the Azores and Madeira, both had overwhelmingly Portuguese populations, and Lisbon subsequently changed their constitutional status from "overseas provinces" to "autonomous regions".
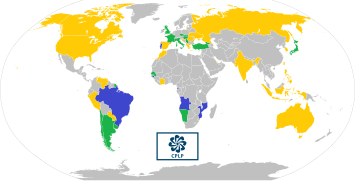
The Community of Portuguese Speaking Countries (CPLP) is the cultural successor of the Empire, analogous to the Commonwealth of Nations for countries formerly part of the British Empire.
Presently, the Community of Portuguese Language Countries (CPLP) serves as the cultural and intergovernmental successor of the Empire.[216]
Macau was returned to China on 20 December 1999, under the terms of an agreement negotiated between People's Republic of China and Portugal twelve years earlier. Nevertheless, the Portuguese language remains co-official with Cantonese Chinese in Macau.[217]
Currently, the Azores and Madeira (the latter administering the uninhabited Savage Islands) are the only overseas territories that remain politically linked to Portugal. Although Portugal began the process of decolonizing East Timor in 1975, during 1999–2002 was sometimes considered Portugal's last remaining colony, as the Indonesian invasion of East Timor was not justified by Portugal.[218]
Eight of the former colonies of Portugal have Portuguese as their official language. Together with Portugal, they are now members of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries, which when combined total 10,742,000 km2, or 7.2% of the Earth's landmass (148 939 063 km2).[219] As at 2023, there are 32 associate observers of the CPLP, reflecting the global reach and influence of Portugal's former empire. Moreover, twelve candidate countries or regions have applied for membership to the CPLP and are awaiting approval.[220]
Today, Portuguese is one of the world's major languages, ranked sixth overall with approximately 240 million speakers around the globe.[221] It is the third most spoken language in the Americas, mainly due to Brazil, although there are also significant communities of Lusophones in nations such as Canada, the US and Venezuela. In addition, there are numerous Portuguese-based creole languages, including the one utilized by the Kristang people in Malacca.[222]
For instance, as Portuguese merchants were presumably the first to introduce the sweet orange in Europe, in several modern Indo-European languages the fruit has been named after them. Some examples are Albanian portokall, Bulgarian портокал (portokal), Greek πορτοκάλι (portokali), Macedonian портокал (portokal), Persian پرتقال (porteghal), and Romanian portocală.[223][224] Related names can be found in other languages, such as Arabic البرتقال (bourtouqal), Georgian ფორთოხალი (p'ort'oxali), Turkish portakal and Amharic birtukan.[223] Also, in southern Italian dialects (e.g., Neapolitan), an orange is portogallo or purtuallo, literally "(the) Portuguese (one)", in contrast to standard Italian arancia.
In light of its international importance, Portugal and Brazil are leading a movement to include Portuguese as one of the official languages of the United Nations.[225]