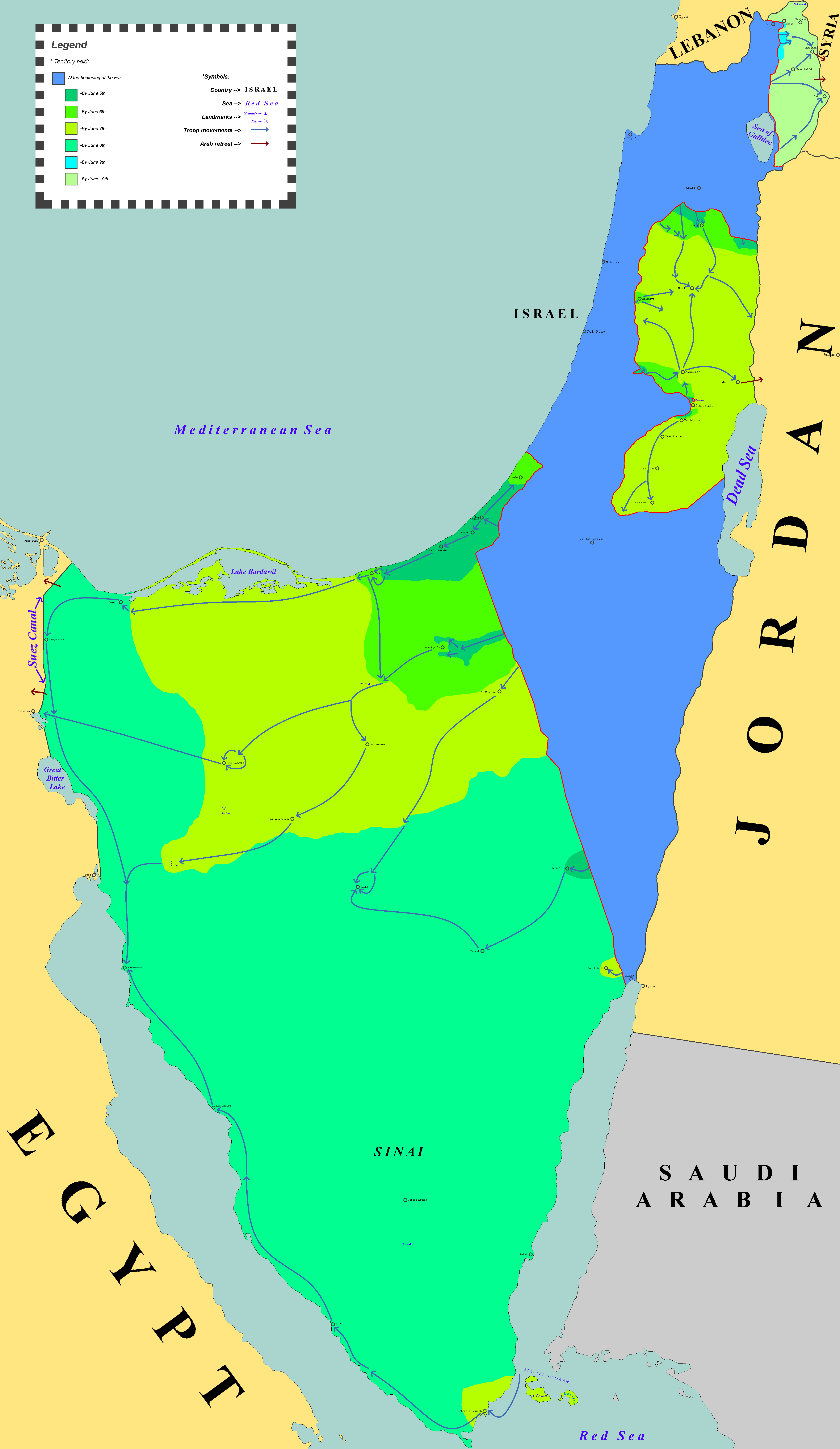
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (Hebrew: מִלְחֶמֶת שֵׁשֶׁת הַיָּמִים, Milḥemet Šešet HaYamim; Arabic: النكسة, an-Naksah, lit. 'The Setback' or حرب 1967, Ḥarb 1967, 'War of 1967') or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967.
For other uses, see Six Day War (disambiguation).
Military hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours, who had been observing the 1949 Armistice Agreements signed at the end of the First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Egypt–Israel border.[34] In the months prior to the outbreak of the Six-Day War in June 1967, tensions again became dangerously heightened: Israel reiterated its post-1956 position that another Egyptian closure of the Straits of Tiran to Israeli shipping would be a definite casus belli. In May 1967, Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser announced that the Straits of Tiran would again be closed to Israeli vessels. He subsequently mobilized the Egyptian military into defensive lines along the border with Israel[35] and ordered the immediate withdrawal of all UNEF personnel.[36][28]
On 5 June 1967, as the UNEF was in the process of leaving the zone, Israel launched a series of preemptive airstrikes against Egyptian airfields and other facilities, launching its war effort.[28] Egyptian forces were caught by surprise, and nearly all of Egypt's military aerial assets were destroyed, giving Israel air supremacy. Simultaneously, the Israeli military launched a ground offensive into Egypt's Sinai Peninsula as well as the Egyptian-occupied Gaza Strip. After some initial resistance, Nasser ordered an evacuation of the Sinai Peninsula; by the sixth day of the conflict, Israel had occupied the entire Sinai Peninsula.[37] Jordan, which had entered into a defense pact with Egypt just a week before the war began, did not take on an all-out offensive role against Israel. However, the Jordanians did launch attacks against Israeli forces to slow Israel's advance.[38] On the fifth day, Syria joined the war by shelling Israeli positions in the north.[39]
Egypt and Jordan agreed to a ceasefire on 8 June, and Syria on 9 June, and it was signed with Israel on 11 June. The Six-Day War resulted in more than 20000 fatal Arab casualties, while Israel suffered almost 1000 fatal casualties. Alongside the combatant casualties were the deaths of 20 Israeli civilians killed in Arab forces air strikes on Jerusalem, 15 UN peacekeepers killed by Israeli strikes in the Sinai at the outset of the war, and 34 US personnel killed in the USS Liberty incident in which Israeli air forces struck a United States Navy technical research ship.
At the time of the cessation of hostilities, Israel had seized Syria's Golan Heights, the Jordanian-annexed West Bank (including East Jerusalem), and Egypt's Sinai Peninsula as well as the Egyptian-occupied Gaza Strip. The displacement of civilian populations as a result of the Six-Day War would have long-term consequences, as around 280000 to 325000 Palestinians and 100000 Syrians fled or were expelled from the West Bank[40] and the Golan Heights, respectively.[41] Nasser resigned in shame following Israel's victory, but was later reinstated following a series of protests across Egypt. In the aftermath of the conflict, Egypt closed the Suez Canal until 1975, eventually leading to the 1970s energy crisis and 1973 oil crisis due to the impact on oil deliveries coming to Europe from the Middle East through the Suez Canal.[42][43]
Armies and weapons
Armies
The Israeli army had a total strength, including reservists, of 264000, though this number could not be sustained during a long conflict, as the reservists were vital to civilian life.[5]
Against Jordan's forces on the West Bank, Israel deployed about 40000 troops and 200 tanks (eight brigades).[71] Israeli Central Command forces consisted of five brigades. The first two were permanently stationed near Jerusalem and were the Jerusalem Brigade and the mechanized Harel Brigade. Mordechai Gur's 55th Paratroopers Brigade was summoned from the Sinai front. The 10th Armored Brigade was stationed north of the West Bank. The Israeli Northern Command comprised a division of three brigades led by Major General Elad Peled which was stationed in the Jezreel Valley to the north of the West Bank.
On the eve of the war, Egypt massed approximately 100000 of its 160000 troops in the Sinai, including all seven of its divisions (four infantry, two armoured and one mechanized), four independent infantry brigades and four independent armoured brigades. Over a third of these soldiers were veterans of Egypt's continuing intervention into the North Yemen Civil War and another third were reservists. These forces had 950 tanks, 1100 APCs, and more than 1000 artillery pieces.[9]
Syria's army had a total strength of 75000 and was deployed along the border with Israel.[12] Professor David W. Lesch wrote that "One would be hard-pressed to find a military less prepared for war with a clearly superior foe" since Syria's army had been decimated in the months and years prior through coups and attempted coups that had resulted in a series of purges, fracturings and uprisings within the armed forces.[72]
The Jordanian Armed Forces included 11 brigades, totalling 55000 troops.[13] Nine brigades (45000 troops, 270 tanks, 200 artillery pieces) were deployed in the West Bank, including the elite armoured 40th, and two in the Jordan Valley. They possessed sizable numbers of M113 APCs and were equipped with some 300 modern Western tanks, 250 of which were U.S. M48 Pattons. They also had 12 battalions of artillery, six batteries of 81 mm and 120 mm mortars,[14] a paratrooper battalion trained in the new U.S.-built school and a new battalion of mechanized infantry. The Jordanian Army was a long-term-service, professional army, relatively well-equipped and well-trained. Israeli post-war briefings said that the Jordanian staff acted professionally, but was always left "half a step" behind by the Israeli moves. The small Royal Jordanian Air Force consisted of only 24 British-made Hawker Hunter fighters, six transport aircraft and two helicopters. According to the Israelis, the Hawker Hunter was essentially on par with the French-built Dassault Mirage III – the IAF's best plane.[73]
One hundred Iraqi tanks and an infantry division were readied near the Jordanian border. Two squadrons of Iraqi fighter-aircraft, Hawker Hunters and MiG 21s, were rebased adjacent to the Jordanian border.[14]
In the weeks leading up to the Six-Day War, Saudi Arabia mobilized forces for deployment to the Jordanian front. A Saudi infantry battalion entered Jordan on 6 June 1967, followed by another on the 8th. Both were based in Jordan's southernmost city, Ma'an. By 17 June, the Saudi contingent in Jordan had grown to include a single infantry brigade, a tank company, two artillery batteries, a heavy mortar company, and a maintenance and support unit. By the end of July 1967, a second tank company and a third artillery battery had been added. These forces remained in Jordan until the end of 1977, when they were recalled for re-equipment and retraining in the Karak region near the Dead Sea.[74][75][76]
The Arab air forces were reinforced by aircraft from Libya, Algeria, Morocco, Kuwait, and Saudi Arabia to make up for the massive losses suffered on the first day of the war. They were also aided by volunteer pilots from the Pakistan Air Force acting in an independent capacity. PAF pilots like Saiful Azam shot down several Israeli planes.[77][78]
Weapons
With the exception of Jordan, the Arabs relied principally on Soviet weaponry. Jordan's army was equipped with American weaponry, and its air force was composed of British aircraft.
Egypt had by far the largest and the most modern of all the Arab air forces, consisting of about 420 combat aircraft,[10][11] all of them Soviet-built and with a large number of top-of-the-line MiG-21s. Of particular concern to the Israelis were the 30 Tu-16 "Badger" medium bombers, capable of inflicting heavy damage on Israeli military and civilian centres.[79]
Israeli weapons were mainly of Western origin. Its air force was composed principally of French aircraft, while its armoured units were mostly of British and American design and manufacture. Some light infantry weapons, including the ubiquitous Uzi, were of Israeli origin.