Anatolia
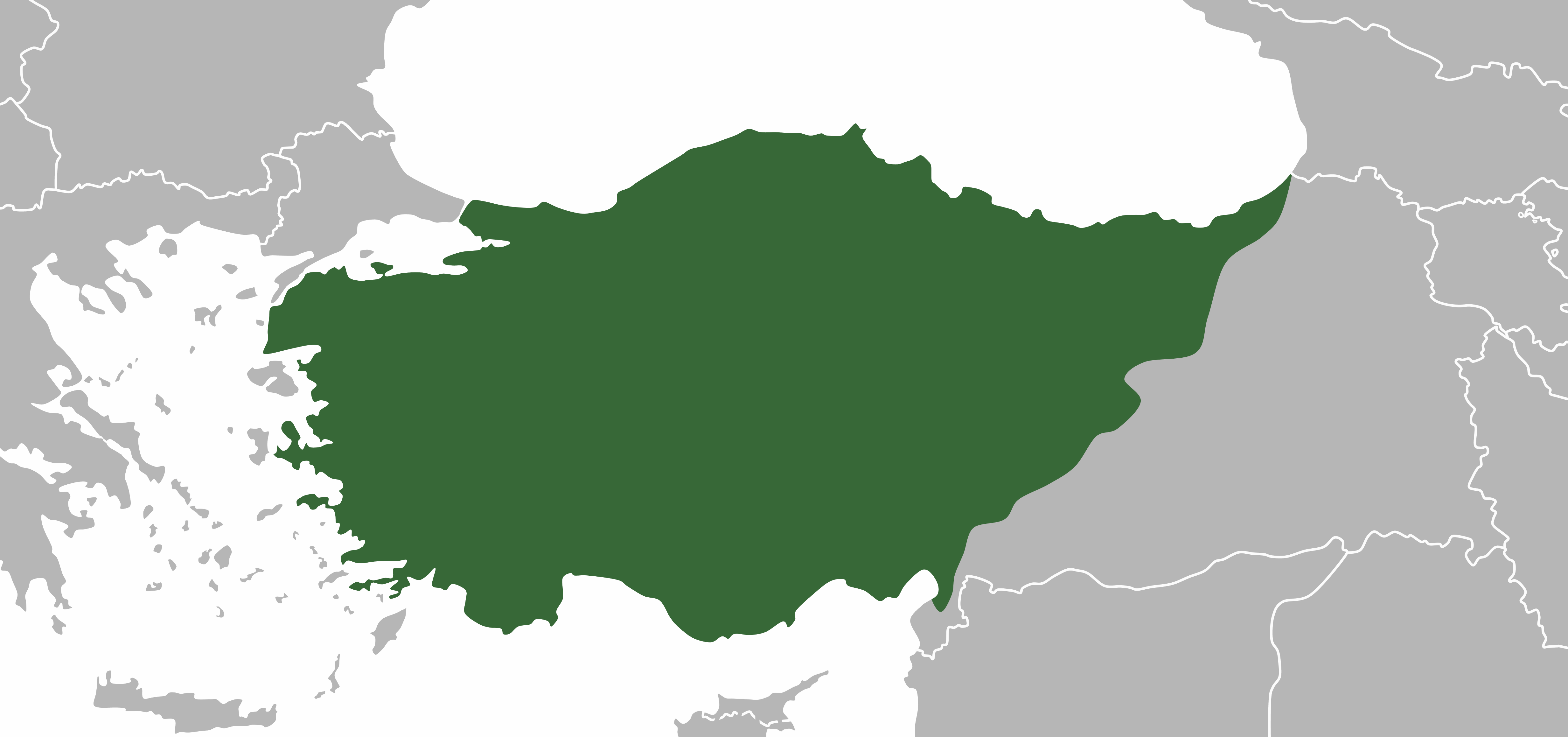
Anatolia (Turkish: Anadolu), also known as Asia Minor,[a] is a large peninsula or a region in Turkey, constituting most of its contemporary territory. Geographically, the Anatolian region is bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the north-west, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern boundary is either the southeastern and eastern borders of Turkey,[1] or an imprecise line from the Gulf of Iskenderun to the Black Sea.[2] Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus strait and the Dardanelles strait, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in the Balkan peninsula of Southeastern Europe.
For other uses, see Anatolia (disambiguation).
Anadolu
"the East", from Greek
756,000 km2 (292,000 sq mi)[3]
(incl. Southeastern and Eastern Anatolia Region)
The ancient Anatolian peoples spoke the now-extinct Anatolian languages of the Indo-European language family, which were largely replaced by the Greek language during classical antiquity as well as during the Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine periods. The major Anatolian languages included Hittite, Luwian, and Lydian, while other, poorly attested local languages included Phrygian and Mysian. Hurro-Urartian languages were spoken in the southeastern kingdom of Mitanni, while Galatian, a Celtic language, was spoken in Galatia, central Anatolia. Ancient peoples in the region included Galatians, Hurrians, Assyrians, Hattians, Cimmerians, as well as Ionian, Dorian, and Aeolic Greeks. The Turkification of Anatolia began under the rule of the Seljuk Empire in the late 11th century, continued under the Ottoman Empire between the late 13th and early 20th centuries, and continues today under the Republic of Turkey. However, various non-Turkic languages continue to be spoken by minorities in Anatolia, including Kurdish, Neo-Aramaic, Armenian, North Caucasian languages, Laz, Georgian, and Greek.
Etymology[edit]
The English-language name Anatolia derives from the Greek Ἀνατολή (Anatolḗ) meaning "the East" and designating (from a Greek point of view) eastern regions in general. The Greek word refers to the direction where the sun rises, coming from ἀνατέλλω anatello '(Ι) rise up', comparable to terms in other languages such as "levant" from Latin levo 'to rise', "orient" from Latin orior 'to arise, to originate', Hebrew מִזְרָח mizraḥ 'east' from זָרַח zaraḥ 'to rise, to shine', Aramaic מִדְנָח midnaḥ from דְּנַח denaḥ 'to rise, to shine'.[17][18]
The use of Anatolian designations has varied over time, perhaps originally referring to the Aeolian, Ionian and Dorian colonies situated along the eastern coasts of the Aegean Sea, but also encompassing eastern regions in general. Such use of Anatolian designations was employed during the reign of Roman Emperor Diocletian (r. 284–305), who created the Diocese of the East, known in Greek as the Eastern Diocese, but completely unrelated to the regions of Asia Minor. In their widest territorial scope, Anatolian designations were employed during the reign of Roman Emperor Constantine I (306–337), who created the Praetorian prefecture of the East, known in Greek as the Eastern Prefecture, encompassing all eastern regions of the Late Roman Empire and spanning from Thrace to Egypt.
Only after the loss of other eastern regions during the 7th century and the reduction of Byzantine eastern domains to Asia Minor, that region became the only remaining part of the Byzantine East, and thus commonly referred to (in Greek) as the Eastern part of the Empire. At the same time, the Anatolic Theme (Ἀνατολικὸν θέμα / "the Eastern theme") was created, as a province (theme) covering the western and central parts of Turkey's present-day Central Anatolia Region, centered around Iconium, but ruled from the city of Amorium.[19][20]
The Latinized form "Anatolia", with its -ia ending, is probably a Medieval Latin innovation.[18] The modern Turkish form Anadolu derives directly from the Greek name Aνατολή (Anatolḗ). The Russian male name Anatoly, the French Anatole and plain Anatol, all stemming from saints Anatolius of Laodicea (d. 283) and Anatolius of Constantinople (d. 458; the first Patriarch of Constantinople), share the same linguistic origin.