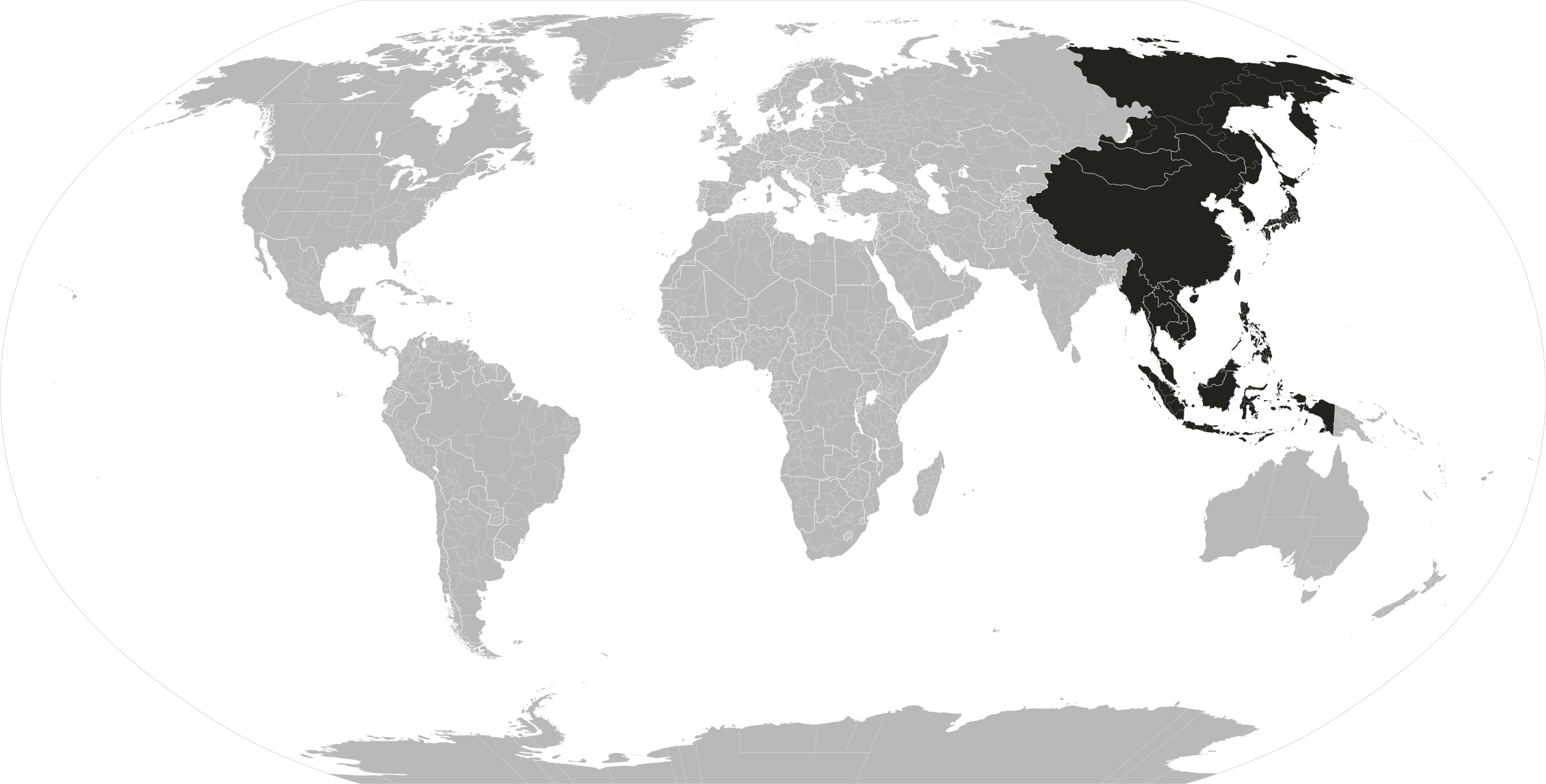
Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including East, North and Southeast Asia.[1][2] South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term.[3][4]
For other uses, see Far East (disambiguation).Far East
遠東
远东
Far East
Yuǎn Dōng
Yuǎn Dōng
Yuǎn Dōng
Jyun5 Dung1
Óan-tong
အရှေ့ဖျား ဒေသ
Viễn Đông
遠東
ตะวันออกไกล
Tawan-ok Klai
극동
極東
Geuk Dong
Geuk Dong
Kŭk Tong
Алс Дорнод
Als Dornod
極東
きょくとう
キョクトウ
Kyoku Tō
Kyoku Tō
تيمور جاءوه
Timur Jauh
Timur Jauh
In Filipino: Kasilangánan
Silangánan (poetic)
Maláyong Silángan (literal)
தூர கிழக்கு
Tūra Kiḻakku
Extremo Oriente
Дальний Восток
IPA: [ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok]
Dál'niy Vostók
ຕາເວັນອອກໄກ
Taven-ok kai
ចុងបូព៌ា
Chong Bopea
Dok Lorosa'e
The term first came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 15th century, particularly the British, denoting the Far East as the "farthest" of the three "Easts", beyond the Near East and the Middle East.[5] Likewise, during the Qing dynasty of the 19th and early 20th centuries, the term "Tàixī (泰西)" – i.e., anything further west than the Arab world – was used to refer to the Western countries.
Since the mid-20th century, the term has mostly gone out of use for the region in international mass media outlets due to its perceived eurocentric connotations.[6][7][8] North Asia is sometimes excluded due to cultural and ethnic differences.[9]
Popularization[edit]
Among Western Europeans, prior to the colonial era, Far East referred to anything further east than the Middle East. In the 16th century, King John III of Portugal called India a "rich and interesting country in the Far East[10] (Extremo Oriente)." The term was popularized during the period of the British Empire as a blanket term for lands to the east of British India.
In pre-World War I European geopolitics, Near East referred to the relatively nearby lands of the Ottoman Empire, Middle East denoted north-western Southern Asian region and Central Asia, and the Far East meant countries along the western Pacific Ocean and eastern Indian Ocean. Many European languages have analogous terms, such as the French (Extrême-Orient), Spanish (Extremo Oriente), Portuguese (Extremo Oriente), Italian (Estremo Oriente), German (Ferner Osten), Polish (Daleki Wschód), Norwegian (Det fjerne Østen) and Dutch (Verre Oosten).